poj 1149 PIGS(最大流+經典構圖)
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-14
PIGS
All data concerning customers planning to visit the farm on that particular day are available to Mirko early in the morning so that he can make a sales-plan in order to maximize the number of pigs sold.
More precisely, the procedure is as following: the customer arrives, opens all pig-houses to which he has the key, Mirko sells a certain number of pigs from all the unlocked pig-houses to him, and, if Mirko wants, he can redistribute the remaining pigs across the unlocked pig-houses.
An unlimited number of pigs can be placed in every pig-house.
Write a program that will find the maximum number of pigs that he can sell on that day.
The next line contains M integeres, for each pig-house initial number of pigs. The number of pigs in each pig-house is greater or equal to 0 and less or equal to 1000.
The next N lines contains records about the customers in the following form ( record about the i-th customer is written in the (i+2)-th line):
A K1 K2 ... KA B It means that this customer has key to the pig-houses marked with the numbers K1, K2, ..., KA (sorted nondecreasingly ) and that he wants to buy B pigs. Numbers A and B can be equal to 0. 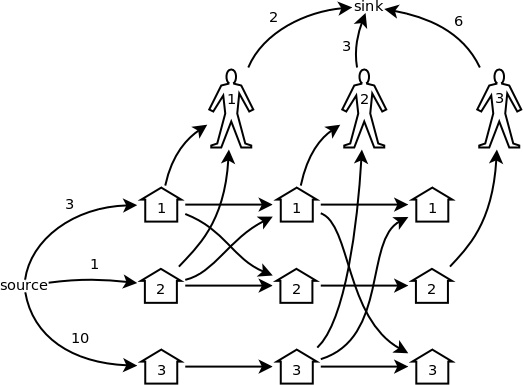 圖 1
不難想像,這個網路模型的最大流量就是最多能賣出的數量。圖中最多有 2 + N + M × N ≈ 100,000 個節點。□
這個模型雖然很直觀,但是節點數太多了,計算速度肯定會很慢。其實不用再想別的演算法,就讓我們繼續上面的例子,用合併的方法來簡化這個網路模型。
首先,最後一輪中沒有開啟的豬圈就可以從圖中刪掉了,也就是中圖2紅色的部分,顯然它們對整個網路的流量沒有任何影響。
圖 1
不難想像,這個網路模型的最大流量就是最多能賣出的數量。圖中最多有 2 + N + M × N ≈ 100,000 個節點。□
這個模型雖然很直觀,但是節點數太多了,計算速度肯定會很慢。其實不用再想別的演算法,就讓我們繼續上面的例子,用合併的方法來簡化這個網路模型。
首先,最後一輪中沒有開啟的豬圈就可以從圖中刪掉了,也就是中圖2紅色的部分,顯然它們對整個網路的流量沒有任何影響。
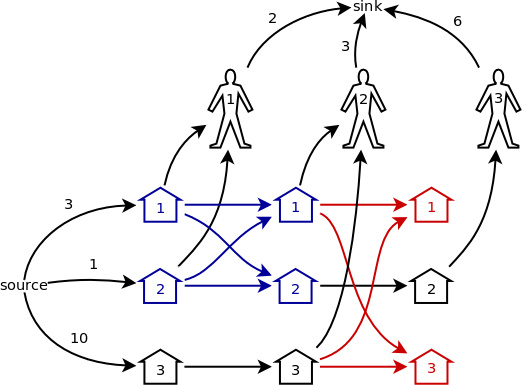 圖 2
接著,看圖 2 中藍色的部分。根據我總結出的以下幾個規律,可以把這 4 個點合併成一個:
規律 1. 如果幾個節點的流量的來源完全相同,則可以把它們合併成一個。
規律 2. 如果幾個節點的流量的去向完全相同,則可以把它們合併成一個。
規律 3. 如果從點 u 到點 v 有一條容量為 +∞ 的邊,並且 u 是 v 的唯一流量來源,或者 v 是 u 的唯一流量去向,則可以把 u 和 v 合併成一個節點。
根據規律1,可以把藍色部分右邊的 1、 2 號節點合併成一個;根據規律2,可以把藍色部分左邊的 1、 2 號節點合併成一個;最後,根據規律3,可以把藍色部分的左邊和右邊(已經分別合併成了一個節點)合併成一個節點。於是,圖2被簡化成了圖3的樣子。也就是說,最後一輪除外,每一輪被開啟的豬圈和下一輪的同樣這些豬圈都可以被合併成一個點。
圖 2
接著,看圖 2 中藍色的部分。根據我總結出的以下幾個規律,可以把這 4 個點合併成一個:
規律 1. 如果幾個節點的流量的來源完全相同,則可以把它們合併成一個。
規律 2. 如果幾個節點的流量的去向完全相同,則可以把它們合併成一個。
規律 3. 如果從點 u 到點 v 有一條容量為 +∞ 的邊,並且 u 是 v 的唯一流量來源,或者 v 是 u 的唯一流量去向,則可以把 u 和 v 合併成一個節點。
根據規律1,可以把藍色部分右邊的 1、 2 號節點合併成一個;根據規律2,可以把藍色部分左邊的 1、 2 號節點合併成一個;最後,根據規律3,可以把藍色部分的左邊和右邊(已經分別合併成了一個節點)合併成一個節點。於是,圖2被簡化成了圖3的樣子。也就是說,最後一輪除外,每一輪被開啟的豬圈和下一輪的同樣這些豬圈都可以被合併成一個點。
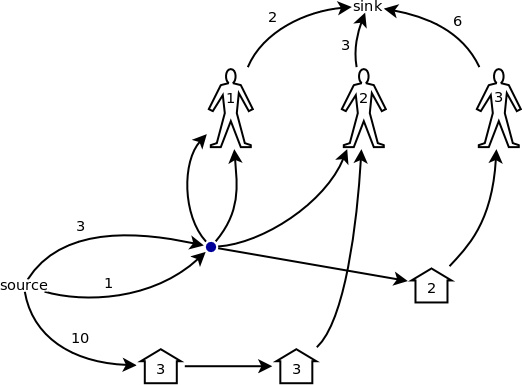 圖 3
圖 3
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K |
| Total Submissions: 14578 | Accepted: 6479 |
Description
Mirko works on a pig farm that consists of M locked pig-houses and Mirko can't unlock any pighouse because he doesn't have the keys. Customers come to the farm one after another. Each of them has keys to some pig-houses and wants to buy a certain number of pigs.All data concerning customers planning to visit the farm on that particular day are available to Mirko early in the morning so that he can make a sales-plan in order to maximize the number of pigs sold.
More precisely, the procedure is as following: the customer arrives, opens all pig-houses to which he has the key, Mirko sells a certain number of pigs from all the unlocked pig-houses to him, and, if Mirko wants, he can redistribute the remaining pigs across the unlocked pig-houses.
An unlimited number of pigs can be placed in every pig-house.
Write a program that will find the maximum number of pigs that he can sell on that day.
Input
The next line contains M integeres, for each pig-house initial number of pigs. The number of pigs in each pig-house is greater or equal to 0 and less or equal to 1000.
The next N lines contains records about the customers in the following form ( record about the i-th customer is written in the (i+2)-th line):
A K1 K2 ... KA B It means that this customer has key to the pig-houses marked with the numbers K1, K2, ..., KA (sorted nondecreasingly ) and that he wants to buy B pigs. Numbers A and B can be equal to 0.
Output
Sample Input
3 3 3 1 10 2 1 2 2 2 1 3 3 1 2 6
Sample Output
7
【題意】:有 M 個豬圈(M ≤ 1000),每個豬圈裡初始時有若干頭豬。開始所有豬圈都是關閉的。依次來了 N 個顧客(N ≤ 100),每個顧客分別會開啟指定的幾個豬圈,從中買若干頭豬。每個顧客分別都有他能夠買的數量的上限。每個顧客走後,他開啟的那些豬圈中的豬,都可以被任意地調換到其它開著的豬圈裡,然後所有豬圈重新關上。 問總共最多能賣出多少頭豬。 【題解】:舉個例子來說。有 3 個豬圈,初始時分別有 3、 1 和 10 頭豬。依次來了 3 個顧客,第一個開啟 1 號 和 2 號豬圈,最多買 2 頭;第二個開啟 1 號 和 3 號豬圈,最多買 3 頭;第三個開啟 2 號豬圈,最多買 6 頭。那麼,最好的可能性之一就是第一個顧客從 1 號圈買 2 頭,然後把 1 號圈剩下的 1 頭放到 2 號圈;第二個顧客從 3 號圈買 3 頭;第三個顧客從 2 號圈買 2 頭。總共賣出 2 + 3 + 2 = 7 頭。□ 不難想像,這個問題的網路模型可以很直觀地構造出來。就拿上面的例子來說,可以構造出圖1所示的模型(圖中凡是沒有標數字的邊,容量都是 +∞):
- 三個顧客,就有三輪交易,每一輪分別都有 3 個豬圈和 1 個顧客的節點。
- 從源點到第一輪的各個豬圈各有一條邊,容量就是各個豬圈裡的豬的初始數量。
- 從各個顧客到匯點各有一條邊,容量就是各個顧客能買的數量上限。
- 在某一輪中,從該顧客開啟的所有豬圈都有一條邊連向該顧客,容量都是 +∞。
- 最後一輪除外,從每一輪的 i 號豬圈都有一條邊連向下一輪的 i 號豬圈,容量都是 +∞,表示這一輪剩下的豬可以留到下一輪。
- 最後一輪除外,從每一輪被開啟的所有豬圈,到下一輪的同樣這些豬圈,兩兩之間都要連一條邊,表示它們之間可以任意流通。
 圖 1
不難想像,這個網路模型的最大流量就是最多能賣出的數量。圖中最多有 2 + N + M × N ≈ 100,000 個節點。□
這個模型雖然很直觀,但是節點數太多了,計算速度肯定會很慢。其實不用再想別的演算法,就讓我們繼續上面的例子,用合併的方法來簡化這個網路模型。
首先,最後一輪中沒有開啟的豬圈就可以從圖中刪掉了,也就是中圖2紅色的部分,顯然它們對整個網路的流量沒有任何影響。
圖 1
不難想像,這個網路模型的最大流量就是最多能賣出的數量。圖中最多有 2 + N + M × N ≈ 100,000 個節點。□
這個模型雖然很直觀,但是節點數太多了,計算速度肯定會很慢。其實不用再想別的演算法,就讓我們繼續上面的例子,用合併的方法來簡化這個網路模型。
首先,最後一輪中沒有開啟的豬圈就可以從圖中刪掉了,也就是中圖2紅色的部分,顯然它們對整個網路的流量沒有任何影響。
 圖 2
接著,看圖 2 中藍色的部分。根據我總結出的以下幾個規律,可以把這 4 個點合併成一個:
規律 1. 如果幾個節點的流量的來源完全相同,則可以把它們合併成一個。
規律 2. 如果幾個節點的流量的去向完全相同,則可以把它們合併成一個。
規律 3. 如果從點 u 到點 v 有一條容量為 +∞ 的邊,並且 u 是 v 的唯一流量來源,或者 v 是 u 的唯一流量去向,則可以把 u 和 v 合併成一個節點。
根據規律1,可以把藍色部分右邊的 1、 2 號節點合併成一個;根據規律2,可以把藍色部分左邊的 1、 2 號節點合併成一個;最後,根據規律3,可以把藍色部分的左邊和右邊(已經分別合併成了一個節點)合併成一個節點。於是,圖2被簡化成了圖3的樣子。也就是說,最後一輪除外,每一輪被開啟的豬圈和下一輪的同樣這些豬圈都可以被合併成一個點。
圖 2
接著,看圖 2 中藍色的部分。根據我總結出的以下幾個規律,可以把這 4 個點合併成一個:
規律 1. 如果幾個節點的流量的來源完全相同,則可以把它們合併成一個。
規律 2. 如果幾個節點的流量的去向完全相同,則可以把它們合併成一個。
規律 3. 如果從點 u 到點 v 有一條容量為 +∞ 的邊,並且 u 是 v 的唯一流量來源,或者 v 是 u 的唯一流量去向,則可以把 u 和 v 合併成一個節點。
根據規律1,可以把藍色部分右邊的 1、 2 號節點合併成一個;根據規律2,可以把藍色部分左邊的 1、 2 號節點合併成一個;最後,根據規律3,可以把藍色部分的左邊和右邊(已經分別合併成了一個節點)合併成一個節點。於是,圖2被簡化成了圖3的樣子。也就是說,最後一輪除外,每一輪被開啟的豬圈和下一輪的同樣這些豬圈都可以被合併成一個點。
 圖 3
圖 3
接著,根據,圖3中的藍色節點、2 號豬圈和 1 號顧客這三點可以合併成一個;圖3中的兩個 3 號豬圈和 2 號顧客也可以合併成一個點。當然,如果兩點之間有多條同向的邊,則這些邊可以合併成一條,容量相加,這個道理很簡單,就不用我多說了。最終,上例中的網路模型被簡化成了圖4 的樣子。
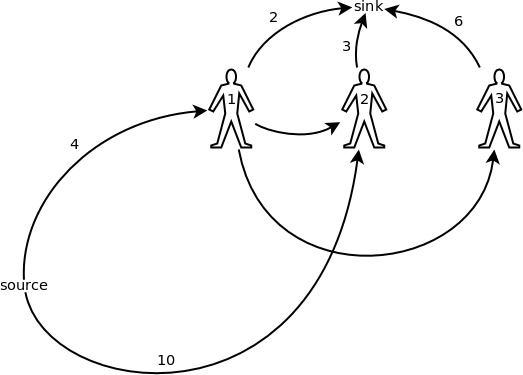
- 每個顧客分別用一個節點來表示。
- 對於每個豬圈的第一個顧客,從源點向他連一條邊,容量就是該豬圈裡的豬的初始數量。如果從源點到一名顧客有多條邊,則可以把它們合併成一條,容量相加。
- 對於每個豬圈,假設有 n 個顧客開啟過它,則對所有整數 i ∈ [1, n),從該豬圈的第 i 個顧客向第 i + 1 個顧客連一條邊,容量為 +∞。
- 從各個顧客到匯點各有一條邊,容量是各個顧客能買的數量上限。
AC程式碼:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdlib>
#define L(rt) (rt<<1)
#define R(rt) (rt<<1|1)
#define ll long long
#define eps 1e-6
using namespace std;
const int INF=1000000000;
const int maxn=1100;
struct Edge{
int u,v,cap,flow,next;
}et[maxn*2];
int low[maxn],cnt[maxn],dis[maxn],cur[maxn],pre[maxn],eh[maxn];
int hcap[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
int n,m,s,t,num;
void init(){
memset(eh,-1,sizeof(eh));
num = 0;
}
void add(int u,int v,int cap,int flow){
Edge e = {u,v,cap,flow,eh[u]};
et[num] = e;
eh[u] = num ++;
}
void addedge(int u,int v,int cap){
add(u,v,cap,0);
add(v,u,0,0);
}
int isap(int s,int t,int nv)
{
int u,v,now,flow = 0;
memset(cnt,0,sizeof(cnt));
memset(dis,0,sizeof(dis));
memset(low,0,sizeof(low));
for(u = 0; u <= nv; u ++) cur[u] = eh[u];
low[s] = INF, cnt[0] = nv, u = s;
while(dis[s]<nv)
{
for(now = cur[u]; now != -1; now = et[now].next)
if(et[now].cap-et[now].flow&&dis[u] == dis[v = et[now].v]+1) break;
if(now != -1)
{
cur[u] = pre[v] = now;
low[v] = min(et[now].cap-et[now].flow,low[u]);
u = v;
if(u == t)
{
for(;u != s; u = et[pre[u]].u)
{
et[pre[u]].flow += low[t];
et[pre[u]^1].flow -= low[t];
}
flow += low[t];
low[s] = INF;
}
}
else
{
if(--cnt[dis[u]] == 0) break;
dis[u] = nv, cur[u] = eh[u];
for(now = eh[u]; now != -1; now = et[now].next)
if(et[now].cap-et[now].flow&&dis[u] > dis[et[now].v]+1)
dis[u] = dis[et[now].v]+1;
cnt[dis[u]] ++;
if(u != s) u = et[pre[u]].u;
}
}
return flow;
}
int main()
{
int nkey,h,cap;
while(~scanf("%d%d",&m,&n))
{
init();
s=0;
t=n+1;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++)
scanf("%d",&hcap[i]);
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
{
scanf("%d",&nkey);
while(nkey --)
{
scanf("%d",&h);
if(!vis[h])
{
vis[h]=true;
addedge(s,i,hcap[h]);
}
else addedge(pre[h],i,INF);
pre[h]=i;
}
scanf("%d",&cap);
addedge(i,t,cap);
}
printf("%d\n",isap(s,t,t+1));
}
return 0;
}
