張季躍 201771010139《面向物件程式設計(java)》第十六週學習總結
張季躍 201771010139《面向物件程式設計(java)》第十六周學習總結
1、實驗目的與要求
(1) 掌握執行緒概念;
(2) 掌握執行緒建立的兩種技術;
(3) 理解和掌握執行緒的優先順序屬性及排程方法;
(4) 掌握執行緒同步的概念及實現技術;
2、實驗內容和步驟
實驗1:測試程式並進行程式碼註釋。
測試程式1:
l 在elipse IDE中除錯執行ThreadTest,結合程式執行結果理解程式;
l 掌握執行緒概念;
l 掌握用Thread的擴充套件類實現執行緒的方法;
l 利用Runnable介面改造程式,掌握用Runnable介面建立執行緒的方法。
| class Lefthand extends Thread { public void run() { for(int i=0;i<=5;i++) { System.out.println("You are Students!"); try{ sleep(500); } catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Lefthand error.");} } } } class Righthand extends Thread { public void run() { for(int i=0;i<=5;i++) { System.out.println("I am a Teacher!"); try{ sleep(300); } catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Righthand error.");} } } } public class ThreadTest { static Lefthand left; static Righthand right; public static void main(String[] args) { left=new Lefthand(); right=new Righthand(); left.start(); right.start(); } } |
程式程式碼:
package Test; class Lefthand implements Runnable { public void run() { for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) { System.out.println("You are Students!"); try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Lefthand error."); } } } } class Righthand implements Runnable { public void run() { for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) { System.out.println("I am a Teacher!"); try { Thread.sleep(300); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Righthand error."); } } } } public class ThreadTest { static Lefthand left; static Righthand right; public static void main(String[] args) { Runnable left1 = new Lefthand(); Runnable right1 = new Righthand() ; Thread left = new Thread(left1); Thread right = new Thread(right1); left.start(); right.start(); } }
實驗結果:
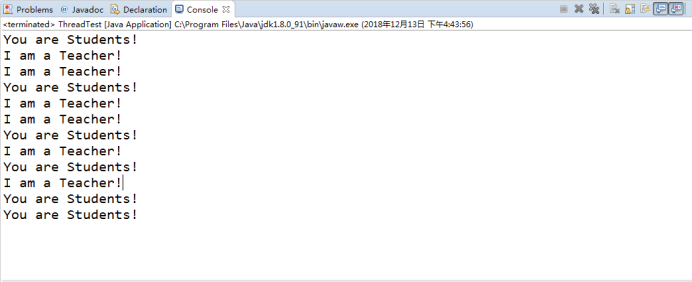
測試程式2:
l 在Elipse環境下除錯教材625頁程式14-1、14-2 、14-3,結合程式執行結果理解程式;
l 在Elipse環境下除錯教材631頁程式14-4,結合程式執行結果理解程式;
l 對比兩個程式,理解執行緒的概念和用途;
l 掌握執行緒建立的兩種技術。
程式程式碼:
package ball; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * Shows an animated bouncing ball. * @version 1.34 2015-06-21 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Bounce { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new BounceFrame(); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }
package balll; import java.awt.*; import java.util.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * The component that draws the balls. * @version 1.34 2012-01-26 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class BallComponent extends JPanel { private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 450; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 350; private java.util.List<Ball> balls = new ArrayList<>(); /** * Add a ball to the component. * @param b the ball to add */ public void add(Ball b) { balls.add(b); } public void paintComponent(Graphics g) { super.paintComponent(g); // erase background Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g; for (Ball b : balls) { g2.fill(b.getShape()); } } public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); } }
package ball; import java.awt.geom.*; /** * A ball that moves and bounces off the edges of a rectangle * @version 1.33 2007-05-17 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Ball { private static final int XSIZE = 15; private static final int YSIZE = 15; private double x = 0; private double y = 0; private double dx = 1; private double dy = 1; /** * Moves the ball to the next position, reversing direction if it hits one of the edges */ public void move(Rectangle2D bounds) { x += dx; y += dy; if (x < bounds.getMinX()) { x = bounds.getMinX(); dx = -dx; } if (x + XSIZE >= bounds.getMaxX()) { x = bounds.getMaxX() - XSIZE; dx = -dx; } if (y < bounds.getMinY()) { y = bounds.getMinY(); dy = -dy; } if (y + YSIZE >= bounds.getMaxY()) { y = bounds.getMaxY() - YSIZE; dy = -dy; } } /** * Gets the shape of the ball at its current position. */ public Ellipse2D getShape() { return new Ellipse2D.Double(x, y, XSIZE, YSIZE); } }
實驗結果:
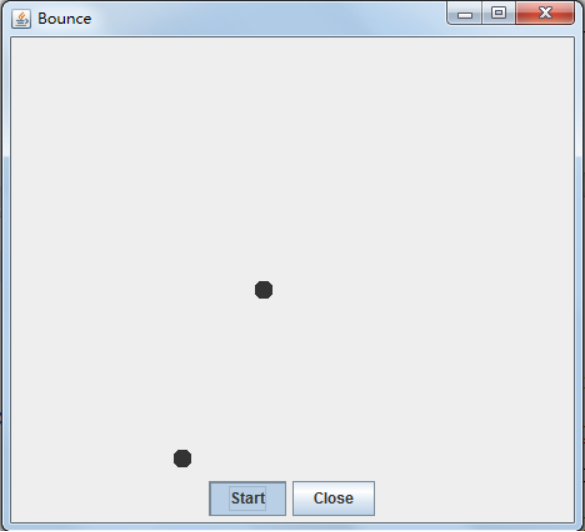
測試程式3:分析以下程式執行結果並理解程式。
| class Race extends Thread { public static void main(String args[]) { Race[] runner=new Race[4]; for(int i=0;i<4;i++) runner[i]=new Race( ); for(int i=0;i<4;i++) runner[i].start( ); runner[1].setPriority(MIN_PRIORITY); runner[3].setPriority(MAX_PRIORITY);} public void run( ) { for(int i=0; i<1000000; i++); System.out.println(getName()+"執行緒的優先順序是"+getPriority()+"已計算完畢!"); } } |
程式程式碼:
class Race extends Thread { public static void main(String args[]) { Race[] runner = new Race[4]; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) runner[i] = new Race(); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) runner[i].start();//使該執行緒開始執行 runner[1].setPriority(MIN_PRIORITY);// 更改執行緒優先順序,執行緒可以具有的最低優先順序 runner[3].setPriority(MAX_PRIORITY);// 更改執行緒的優先順序,執行緒可以具有的最高優先順序 } public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++);// 延時作用 System.out.println(getName() + "執行緒的優先順序是" + getPriority() + "已計算完畢!"); } }
測試結果:
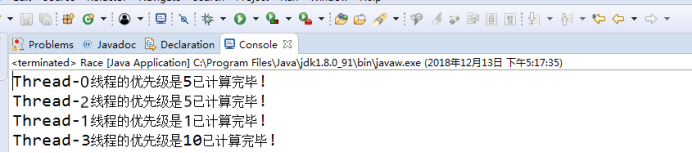
測試程式4
l 教材642頁程式模擬一個有若干賬戶的銀行,隨機地生成在這些賬戶之間轉移錢款的交易。每一個賬戶有一個執行緒。在每一筆交易中,會從執行緒所服務的賬戶中隨機轉移一定數目的錢款到另一個隨機賬戶。
l 在Elipse環境下除錯教材642頁程式14-5、14-6,結合程式執行結果理解程式;
程式程式碼:
package unsynch; import java.util.*; /** * A bank with a number of bank accounts. * * @version 1.30 2004-08-01 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Bank { private final double[] accounts; /** * Constructs the bank. * * @param n the number of accounts * @param initialBalance the initial balance for each account */ public Bank(int n, double initialBalance) { accounts = new double[n]; Arrays.fill(accounts, initialBalance); } /** * Transfers money from one account to another. * * @param from the account to transfer from * @param to the account to transfer to * @param amount the amount to transfer */ public void transfer(int from, int to, double amount) { if (accounts[from] < amount) return; System.out.print(Thread.currentThread());//返回對當前正在執行的執行緒物件的引用 accounts[from] -= amount; System.out.printf(" %10.2f from %d to %d", amount, from, to); accounts[to] += amount; System.out.printf(" Total Balance: %10.2f%n", getTotalBalance()); } /** * Gets the sum of all account balances. * * @return the total balance */ public double getTotalBalance() { double sum = 0; for (double a : accounts) sum += a; return sum; } /** * Gets the number of accounts in the bank. * * @return the number of accounts */ public int size() { return accounts.length; } }
package unsynch; /** * This program shows data corruption when multiple threads access a data * structure. * * @version 1.31 2015-06-21 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class UnsynchBankTest { public static final int NACCOUNTS = 100; public static final double INITIAL_BALANCE = 1000; public static final double MAX_AMOUNT = 1000; public static final int DELAY = 10; public static void main(String[] args) { Bank bank = new Bank(NACCOUNTS, INITIAL_BALANCE); for (int i = 0; i < NACCOUNTS; i++) { int fromAccount = i; Runnable r = () -> { try { while (true) { int toAccount = (int) (bank.size() * Math.random()); double amount = MAX_AMOUNT * Math.random(); bank.transfer(fromAccount, toAccount, amount); Thread.sleep((int) (DELAY * Math.random()));//在指定的毫秒數內讓當前正在執行的執行緒休眠 } } catch (InterruptedException e) { } }; Thread t = new Thread(r);//分配新的 Thread 物件 t.start();//使該執行緒開始執行 } } }
測試結果:

綜合程式設計練習
程式設計練習1
- 設計一個使用者資訊採集程式,要求如下:
(1) 使用者資訊輸入介面如下圖所示:
(2) 使用者點選提交按鈕時,使用者輸入資訊顯示控制檯介面;
(3) 使用者點選重置按鈕後,清空使用者已輸入資訊;
(4) 點選視窗關閉,程式退出。
實驗程式碼:
package 測試程式5; import java.awt.EventQueue; import javax.swing.JFrame; public class Mian { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { demo page = new demo(); }); } }
package 測試程式5; import java.awt.Dimension; import java.awt.Toolkit; import java.awt.Window; public class WinCenter { public static void center(Window win){ Toolkit tkit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit(); Dimension sSize = tkit.getScreenSize(); Dimension wSize = win.getSize(); if(wSize.height > sSize.height){ wSize.height = sSize.height; } if(wSize.width > sSize.width) { wSize.width = sSize.width; } win.setLocation((sSize.width - wSize.width)/ 2, (sSize.height - wSize.height)/ 2); } }
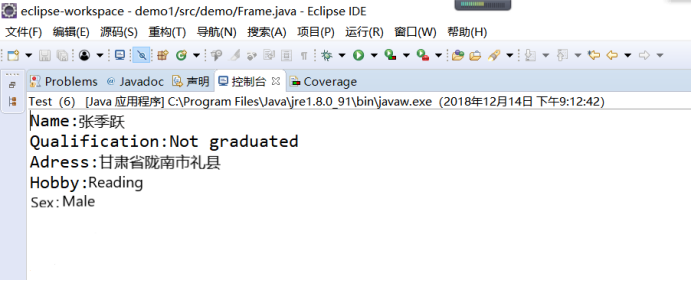
package 測試程式5; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; import javax.swing.border.*; public class demo extends JFrame { public demo() { JPanel panel1 = new JPanel(); panel1.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 45)); panel1.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 4)); JLabel label1 = new JLabel("Name:"); JTextField j1 = new JTextField(""); JLabel label2 = new JLabel("Qualification:"); JComboBox<Object> j2 = new JComboBox<>(); j2.addItem("Graduate"); j2.addItem("Not Graduate"); panel1.add(label1); panel1.add(j1); panel1.add(label2); panel1.add(j2); JPanel panel2 = new JPanel(); panel2.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 50)); panel2.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 4)); JLabel label3 = new JLabel("Address:"); JTextArea j3 = new JTextArea(); JLabel label4 = new JLabel("Hobby:"); JPanel p = new JPanel(); p.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 1)); p.setBorder(BorderFactory.createLineBorder(null)); JCheckBox c1 = new JCheckBox("Reading"); JCheckBox c2 = new JCheckBox("Singing"); JCheckBox c3 = new JCheckBox("Dancing"); p.add(c1); p.add(c2); p.add(c3); panel2.add(label3); panel2.add(j3); panel2.add(label4); panel2.add(p); JPanel panel3 = new JPanel(); panel3.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 150)); FlowLayout flowLayout1 = new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT, 20, 40); panel3.setLayout(flowLayout1); JLabel label5 = new JLabel("Sex:"); JPanel p1 = new JPanel(); p1.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,1)); p1.setBorder(BorderFactory.createLineBorder(null)); ButtonGroup bu = new ButtonGroup(); JRadioButton jr1 = new JRadioButton("Male"); JRadioButton jr2 = new JRadioButton("Female"); bu.add(jr1); bu.add(jr2); p1.add(jr1); p1.add(jr2); panel3.add(label5); panel3.add(p1); add(panel1); add(panel2); add(panel3); JPanel panel4 = new JPanel(); panel4.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 150)); JButton b1 = new JButton("Validate"); panel4.add(b1); JButton b2 = new JButton("Reset"); panel4.add(b2); add(panel4); FlowLayout flowLayout = new FlowLayout(); this.setLayout(flowLayout); this.setTitle("Students Detail"); this.setBounds(200, 200, 800, 400); this.setVisible(true); this.setDefaultCloseOperation(DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE); b1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { // TODO 自動生成的方法存根 String xueli = j2.getSelectedItem().toString(); System.out.println("Name:" + j1.getText()); System.out.println("Qualification:" + xueli); String hobbystring = "Hobby:"; if (c1.isSelected()) { hobbystring += "Reading"; } if (c2.isSelected()) { hobbystring += "Singing"; } if (c3.isSelected()) { hobbystring += "Dancing"; } System.out.println("Address:" + j3.getText()); if (jr1.isSelected()) { System.out.println("Sex:Male"); } if (jr2.isSelected()) { System.out.println("Sex:Female"); } System.out.println(hobbystring); } }); b2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { // TODO 自動生成的方法存根 j1.setText(null); j3.setText(null); j2.setSelectedIndex(0); c1.setSelected(false); c2.setSelected(false); c3.setSelected(false); bu.clearSelection(); } }); } public static void main(String args[]) { new demo(); } }
實驗結果:
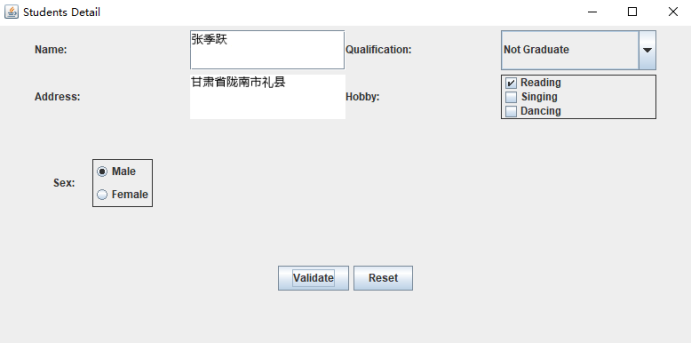
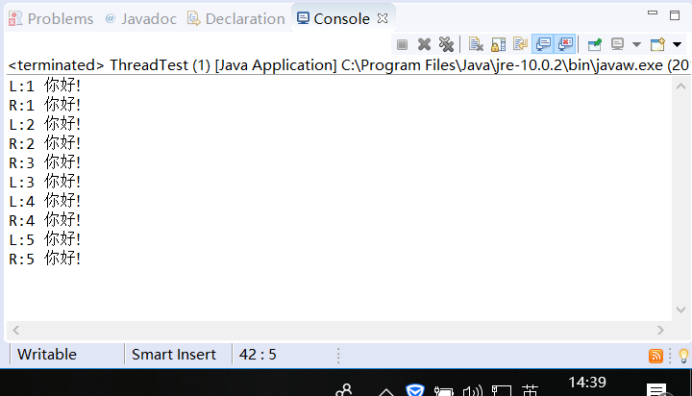
2.建立兩個執行緒,每個執行緒按順序輸出5次“你好”,每個“你好”要標明來自哪個執行緒及其順序號。
實驗程式碼:
package demo; class Lefthand extends Thread { public void run() { for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { System.out.println("L:"+i+" 你好!"); try { sleep(300); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Lefthand error."); } } } } class Righthand extends Thread{ public void run() { for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { System.out.println("R:"+i+" 你好!"); try { sleep(300); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Righthand error."); } } } } public class ThreadTest { static Lefthand left; static Righthand right; public static void main(String[] args) { left = new Lefthand(); right = new Righthand(); left.start(); right.start(); } }
實驗結果:
3. 完善實驗十五 GUI綜合程式設計練習程式。
實驗總結:
在這一週的學習過程中,我初步瞭解學習了關於執行緒的知識,並初步掌握了執行緒建立的兩種方法,但在實驗過程中,我發現我對執行緒掌握的並不是很熟練,實驗二還好說,但實驗一有很多不懂的地方,還是參考了許多同學的程式碼才做出來,即使如此,與要求的結果還是有許多的不同。
