【Linux】建立邏輯卷管理(LVM)
LVM是對磁碟進行分割槽管理的機制。LVM有很多優點:線上擴容,跨磁碟分割槽......,缺點:管理相對麻煩。建立LVM的過程如下:
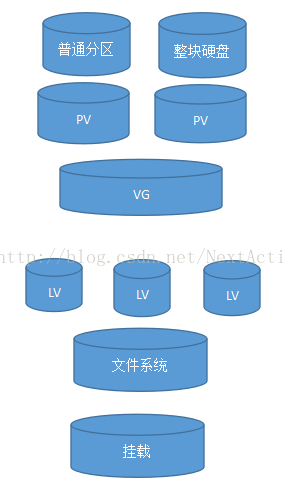
LVM是基於普通分割槽或者整塊硬碟來進行的。我們首先把這些儲存轉換為PV(physical volumn 物理卷),其次把PV加入到VG(volumn group 卷組),再從卷組中劃分LV(logical volumn 邏輯卷),然後把LV格式化為檔案系統,最後掛載使用。
實驗描述:使用sdb、sdc兩塊硬碟配置LVM
實驗過程:
一、配置PV物理卷
1.檢視磁碟情況
[[email protected] ~]# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/sda: 42.9 GB, 42949672960 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 5221 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 1 13 104391 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 14 535 4192965 82 Linux swap / Solaris
/dev/sda3 536 5221 37640295 83 Linux
Disk /dev/sdb: 5368 MB, 5368709120 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 652 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Disk /dev/sdb doesn't contain a valid partition table
Disk /dev/sdc: 5368 MB, 5368709120 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 652 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Disk /dev/sdc doesn't contain a valid partition table
2.對sdb、sdc進行分割槽(我這裡把sdb、sdc各只分了一個主分割槽)
[[email protected] ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb
Device contains neither a valid DOS partition table, nor Sun, SGI or OSF disklabel
Building a new DOS disklabel. Changes will remain in memory only,
until you decide to write them. After that, of course, the previous
content won't be recoverable.
Warning: invalid flag 0x0000 of partition table 4 will be corrected by w(rite)
Command (m for help): n
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
p
Partition number (1-4): 1
First cylinder (1-652, default 1):
Using default value 1
Last cylinder or +size or +sizeM or +sizeK (1-652, default 652):
Using default value 652
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
WARNING: Re-reading the partition table failed with error 16: Device or resource busy.
The kernel still uses the old table.
The new table will be used at the next reboot.
Syncing disks.
[[email protected] ~]# fdisk /dev/sdc
Device contains neither a valid DOS partition table, nor Sun, SGI or OSF disklabel
Building a new DOS disklabel. Changes will remain in memory only,
until you decide to write them. After that, of course, the previous
content won't be recoverable.
Warning: invalid flag 0x0000 of partition table 4 will be corrected by w(rite)
Command (m for help): n
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
p
Partition number (1-4): 1
First cylinder (1-652, default 1):
Using default value 1
Last cylinder or +size or +sizeM or +sizeK (1-652, default 652):
Using default value 652
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
3.分割槽 system格式為linux LVM
[[email protected] ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb
Command (m for help): t
Selected partition 1
Hex code (type L to list codes):8e
Changed system type of partition 1 to 8e (Linux LVM)
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
[[email protected] ~]#
[[email protected] ~]# fdisk /dev/sdc
Command (m for help): t
Selected partition 1
Hex code (type L to list codes):8e
Changed system type of partition 1 to 8e (Linux LVM)
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
[[email protected] ~]#
[[email protected] ~]# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/sda: 42.9 GB, 42949672960 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 5221 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 1 13 104391 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 14 535 4192965 82 Linux swap / Solaris
/dev/sda3 536 5221 37640295 83 Linux
Disk /dev/sdb: 5368 MB, 5368709120 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 652 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 652 5237158+ 8e Linux LVM
Disk /dev/sdc: 5368 MB, 5368709120 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 652 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdc1 1 652 5237158+ 8e Linux LVM
4.建立物理卷PV
[[email protected] ~]# pvcreate /dev/sdb1
Physical volume "/dev/sdb1" successfully created
[[email protected] ~]# pvcreate /dev/sdc1
Physical volume "/dev/sdc1" successfully created
[[email protected] ~]# pvs
PV VG Fmt Attr PSize PFree
/dev/sdb1 lvm2 a- 4.99G 4.99G
/dev/sdc1 lvm2 a- 4.99G 4.99G
[[email protected] ~]# pvdisplay
--- Physical volume ---
PV Name /dev/sdb1
VG Name vgdata
PV Size 4.99 GB / not usable 2.41 MB
Allocatable yes
PE Size (KByte) 4096
Total PE 1278
Free PE 1278
Allocated PE 0
PV UUID yGtlcJ-EVvu-ZRXA-RKhh-xGz7-Br8K-By2zdr
--- Physical volume ---
PV Name /dev/sdc1
VG Name vgdata
PV Size 4.99 GB / not usable 2.41 MB
Allocatable yes
PE Size (KByte) 4096
Total PE 1278
Free PE 1278
Allocated PE 0
PV UUID DzbU8c-3gZ7-8dup-mAH1-K4Vn-hHU9-Jfimtl
二、建立卷組VG
建立命令:vgcreate VG名稱 PV絕對路徑
[[email protected] ~]# vgcreate vgdata /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc1
Volume group "vgdata" successfully created
[[email protected] ~]# vgs
VG #PV #LV #SN Attr VSize VFree
vgdata 2 0 0 wz--n- 9.98G 9.98G
[[email protected] ~]# vgdisplay
--- Volume group ---
VG Name vgdata
System ID
Format lvm2
Metadata Areas 2
Metadata Sequence No 1
VG Access read/write
VG Status resizable
MAX LV 0
Cur LV 0
Open LV 0
Max PV 0
Cur PV 2
Act PV 2
VG Size 9.98 GB
PE Size 4.00 MB
Total PE 2556
Alloc PE / Size 0 / 0
Free PE / Size 2556 / 9.98 GB
VG UUID qR2txF-XLix-1BYn-ei9A-KFjZ-0kcA-4fITDn
三、建立邏輯卷LV
建立命令:lvcreate {選項} 卷組名
一般為:lvcreate -L 【size】 【lvname】【vgname】
建立一個5G的名為lv1的邏輯卷:
[[email protected] ~]# lvcreate -L 5G -n lv1 vgdata
Logical volume "lv1" created
[[email protected] ~]# lvs
LV VG Attr LSize Origin Snap% Move Log Copy% Convert
lv1 vgdata -wi-a- 5.00G
[[email protected] ~]# lvdisplay
--- Logical volume ---
LV Name /dev/vgdata/lv1
VG Name vgdata
LV UUID vcJTYO-IHkM-k7ju-x8C1-jmCR-pVKN-3dO5Dm
LV Write Access read/write
LV Status available
# open 0
LV Size 5.00 GB
Current LE 1280
Segments 2
Allocation inherit
Read ahead sectors auto
- currently set to 256
Block device 253:0
四、格式化建立檔案系統
[[email protected] ~]# mkfs.ext3 /dev/vgdata/lv1
mke2fs 1.39 (29-May-2006)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
655360 inodes, 1310720 blocks
65536 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=1342177280
40 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
16384 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (32768 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 21 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
五、掛載邏輯卷
[[email protected] ~]# mkdir /u02
[[email protected] ~]# mount /dev/vgdata/lv1 /u02
[[email protected] ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda3 35G 13G 21G 38% /
/dev/sda1 99M 22M 73M 23% /boot
tmpfs 995M 0 995M 0% /dev/shm
/dev/mapper/vgdata-lv1
5.0G 139M 4.6G 3% /u02
相關推薦
【Linux】建立邏輯卷管理(LVM)
LVM是對磁碟進行分割槽管理的機制。LVM有很多優點:線上擴容,跨磁碟分割槽......,缺點:管理相對麻煩。建立LVM的過程如下: LVM是基於普通分割槽或者整塊硬碟來進行的。我們首先把這些儲存
Linux邏輯卷管理(LVM)
一、邏輯卷(LV)、卷組(VG)、物理卷(PV)關係 邏輯卷(LV)是卷組(VG)的一部分,可以在卷組大小內動態增加,每個卷組可分為多個邏輯卷。 卷組由多個物理卷(PV)組成。 每個物理卷是一個塊裝置(磁碟分割槽等)。 二、LVM儲存 1.準備物理裝置 可以是磁
【Linux】mv根目錄的恢復(轉)
lin 登陸 logs har 指定 工具 參數 所有 沒有 一次錯誤mv /* /path/to 操作的恢復 描述:執行mv命令的時候沒有註意路徑,結果把根目錄下的大部分目錄都挪到了一個新路徑中,然後立即 出錯命令不能繼續,因為 /lib已經被挪走了,/lib下保存有
HP UNIX--檔案系統和邏輯卷管理(一)
最近接手的一庫在HP-UNIX上,之前沒玩過,甚至心裡還抱怨怎麼HP-UNIX的df-g這麼難看,還得現計算大小,被同事狠狠鄙視了一番。今天無意搜出一篇比較完整的HP-UNIX檔案系統管理的文章,轉載一下,以便檢視。感謝博主:http://yls_forever.blog.
Linux邏輯盤卷管理(LogicalVolumeManager)
LVM是邏輯盤卷管理(LogicalVolumeManager)的簡稱,它是Linux環境下對磁碟分割槽進行管理的一種機制,LVM是建立在硬碟和 分割槽之上的一個邏輯層,來提高磁碟分割槽管理的靈活性。通過LVM系統管理員可以輕鬆管理磁碟分割槽,如:將若干個磁碟分割槽連線為
【Linux】命令——網絡管理
改ip sta body ifconfig 掩碼 查看 net ping nbsp ping IP 測試網絡 ifconfig 查看IP ifconfig 網卡 IP netmask 掩碼 臨時修改IP netstat 查看端口 【Linux】
【Linux】---基本的使用者管理命令及系統管理操作
---------常用的使用者管理命令 ********建立一個使用者的命令: 1.useradd beat ********需要為其設定一個密碼: 2.passwd beat 預設建立的使用者在root許可權下的
【Linux】---vmware虛擬網路配置(NAT模式)及不能ping通主機和百度
nat模式配置 nat模式配置,虛擬機器可以訪問百度 首先本機閘道器不能喝VMNET8一個閘道器 本機的IP及閘道器 VMnet8的設定 虛擬機器編輯器設定,需要和VMnet8在同一個閘道器下 虛擬機器的設定 此
【 Linux 】建立、檢視、刪除檔案
目錄 建立並檢視 單個刪除 從小白開始,記錄每一次遇到的問題,然後整理出來,我相信剛接觸Linux的人多多少少也會遇到類似的問題,如果看到了我的部落格,也是一種緣分。 今天想記錄下如何建立,檢視,以及刪除一個檔案。 建立並檢視 首先看看最普通的辦法,純粹使
【linux】建立軟連結
linux下的軟連結類似於windows下的快捷方式 ln -s python3 python 如上所示:建立python3的軟連線python,其中python3是已經存在的原檔案,python是還沒有建立的連結名,其作用是進入了python就等於是進入了python3了。 刪除軟
【Linux】CentOS 6.5 伺服器(虛擬機器)搭建過程
一、安裝介質準備 1、 CentOS 6.5 的安裝映象分為兩張 DVD 光碟(Bin 安裝版,非 LiveCD) 注:DVD1 內包含了系統檔案及大部分常用軟體安裝包,DVD2 為額外的軟體安裝包,安裝系統時可只准備 DVD1;實驗環境搭建本地源建議兩張光碟全部
用kickstart建立邏輯卷管理LVM分割槽
建立兩個物理分割槽分別給Boot和Swap分割槽,剩餘的空間作LVM。 Partition Size Name------------------------------/boot &nbs
【轉】實現新建多級目錄(樹形)linux-c語言
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include<sys/stat.h> int Create
【Linux】高併發伺服器模型(多程序模型和多執行緒模型)
多程序併發伺服器 使用多程序併發伺服器時要考慮以下幾點: 1. 父程序最大檔案描述個數(父程序中需要close關閉accept返回的新檔案描述符) 2. 系統內建立程序個數(與記憶體大小相關)
【原創】IP攝像頭技術縱覽(一)---linux 核心編譯,USB攝像頭裝置識別
IP攝像頭技術縱覽(一)— linux 核心編譯,USB攝像頭裝置識別 開始正文之前先來認識一下我的開發環境: 系統:ubuntu 10.04 開發板:AT91SAM9260 + Linux-2.6.30 USB攝像頭:UVC無驅攝像頭(著手開發時只
【STM32】NVIC中斷優先順序管理(中斷向量表)
STM32F1xx官方資料:《STM32中文參考手冊V10》-第9章 中斷和事件Cortex-M3核心支援256箇中斷,其中包含了16個核心中斷(異常)和240個外部中斷,並且具有256級的可程式設計中斷設定。但是,STM32並沒有使用CM3核心的全部東西,而是隻用了它的一部
磁碟管理之邏輯卷管理(Logical Volume Manager)
LVM是邏輯卷管理(Logical Volume Manager)的簡稱,它是建立在物理儲存裝置之上的一個抽象層,允許你生成邏輯儲存卷,與直接使用物理儲存在管理上相比,提供了更好靈活性。 LVM將儲存虛擬化,使用邏輯卷,你不會受限於物理磁碟的大小,另外,與硬體相關的儲存
linux下建立邏輯卷命令
fdisk -uv dev/sda 按n新增分割槽 按t 改變分割槽id 按w儲存退出 partx -a /dev/sda pvcreate /dev/sda6 vgcreate myvg(邏輯卷名稱)/dev/sda6 lvcreate -L 200M - lvtest
【OpenGL】Shader實例分析(七)- 雪花飄落效果
mouse llb cto 接下來 pix lan details effect art 轉發請保持地址:http://blog.csdn.net/stalendp/article/details/40624603 研究了一個雪花飄落效果。感覺挺不錯的。分享給大家,效
【開源】OSharp框架學習系列(1):總體設計及系列導航
正是 html 組織 內聚性 權限 是什麽 enc 3-0 分發 OSharp是什麽? OSharp是個快速開發框架,但不是一個大而全的包羅萬象的框架,嚴格的說,OSharp中什麽都沒有實現。與其他大而全的框架最大的不同點,就是OSharp只做抽象封裝,不做實現。依賴註
