Java資料結構----棧(Stack)原始碼分析和個人簡單實現
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-10
一、Stack原始碼分析
1.繼承結構
棧是資料結構中一種很重要的資料結構型別,因為棧的後進先出功能是實際的開發中有很多的應用場景。Java API中提供了棧(Stacck)的實現。
Stack類繼承了Vector類,而Vector類繼承了AbstractList抽象類,實現了List介面,Cloneable介面,RandomAcces介面以及Serializable介面,需要指出的Vector內部還有兩個內部類ListItr和Itr,Itr在繼承Vector的同時實現了Iterator介面,而ListItr在繼承了Itr類的同時實現了ListIterator介面。
2、圖解
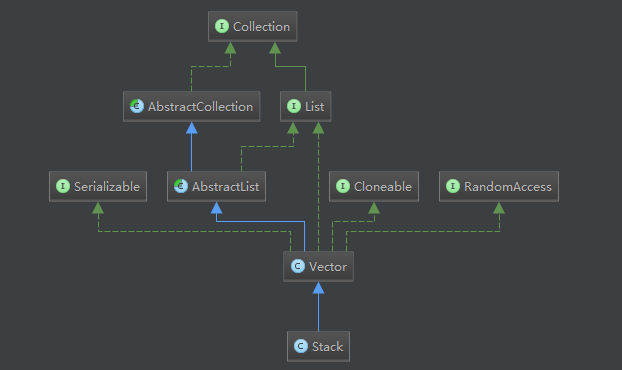
3、原始碼分析
Stack類裡的方法:
1).public Stack() //一個無參構造方法,能直接建立一個Stack
2).public E push(E item) //向棧頂壓入一個項
3).public synchronized E pop() //移走棧頂物件,將該物件作為函式值返回
4).public synchronized E peek() //查詢棧頂物件,而不從棧中移走。
5).public boolean empty() //測試棧是否為空
6).public synchronized int search(Object o) //返回棧中物件的位置,從1開始。
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1224463164541339165L;
其他值的方法是從Vector類繼承而來,通過原始碼可以發現Vector有幾個屬性值:
protected Object[] elementData //elementData用於儲存Stack中的每個元素;
protected int elementCount //elementCount用於動態的儲存元素的個數,即實際元素個數
protected int capacityIncrement //capacityIncrement用來儲存Stack的容量(一般情況下應該是大於elementCount)
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = 2147483639 ; //MAX_ARRAY_SIZE 用於限制Stack能夠儲存的最大值數量
通過這幾屬性我們可以發現,Stack底層是採用陣列
1、public E push(E item) //向棧頂壓入一個項
2、public synchronized E peek() //查詢棧頂物件,而不從棧中移走//向棧頂壓入一個項 public E push(E item) { //呼叫Vector類裡的新增元素的方法 addElement(item); return item; } public synchronized void addElement(E obj) { //通過記錄modCount引數來實現Fail-Fast機制 modCount++; //確保棧的容量大小不會使新增的資料溢位 ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1); elementData[elementCount++] = obj; } private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) { //防止溢位。超出了陣列可容納的長度,需要進行動態擴充套件!!! if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); } //陣列動態增加的關鍵所在 private void grow(int minCapacity) { // overflow-conscious code int oldCapacity = elementData.length; //如果是Stack的話,陣列擴充套件為原來的兩倍 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ? capacityIncrement : oldCapacity); //擴充套件陣列後需要判斷兩次 //第1次是新陣列的容量是否比elementCount + 1的小(minCapacity;) if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; //第1次是新陣列的容量是否比指定最大限制Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8 大 //如果大,則minCapacity過大,需要判斷下 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } //檢查容量的int值是不是已經溢位 private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow throw new OutOfMemoryError(); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; }
//查詢棧頂物件,而不從棧中移走。
public synchronized E peek() {
int len = size();
if (len == 0)
throw new EmptyStackException();
return elementAt(len - 1);
}
//Vector裡的方法,獲取實際棧裡的元素個數
public synchronized int size() {
return elementCount;
}
public synchronized E elementAt(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
//陣列下標越界異常
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " + elementCount);
}
//返回資料下標為index的值
return elementData(index);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}3、public synchronized E pop() //移走棧頂物件,將該物件作為函式值返回
//移走棧頂物件,將該物件作為函式值返回
public synchronized E pop() {
E obj;
int len = size();
obj = peek();
//len-1的得到值就是陣列最後一個數的下標
removeElementAt(len - 1);
return obj;
}
//Vector裡的方法
public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
modCount++;
//陣列下標越界異常出現的情況
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " + elementCount);
} else if (index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
//陣列中index以後的元素個數,由於Stack呼叫的該方法,j始終為0
int j = elementCount - index - 1;
if (j > 0) {
// 陣列中index以後的元素,整體前移,(這個方法挺有用的!!)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);
}
elementCount--;
elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
}4.public boolean empty() //測試棧是否為空
public boolean empty() {
return size() == 0;
}5.public synchronized int search(Object o) //返回棧中物件的位置,從1開始。
// 返回棧中物件的位置,從1開始。如果物件o作為項在棧中存在,方法返回離棧頂最近的距離。
//棧中最頂部的項被認為距離為1。
public synchronized int search(Object o) {
//lastIndexOf返回一個指定的字串值最後出現的位置,
//在一個字串中的指定位置從後向前搜尋
int i = lastIndexOf(o);
if (i >= 0) {
//所以離棧頂最近的距離需要相減
return size() - i;
}
return -1;
}
//Vector裡的方法
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
return lastIndexOf(o, elementCount-1);
}
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o, int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= "+ elementCount);
//Vector、Stack裡可以放null資料
if (o == null) {
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}二、個人簡單實現
棧單鏈表實現:沒有長度限制,並且出棧和入棧速度都很快
public class LinkedListStack {
<pre name="code" class="java"> private LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
//入棧
public void push(Object obj) {
linkedList.insertHead(obj);
}
<pre name="code" class="java"> //向棧頂壓入一個項
public E push(E item) {
//呼叫Vector類裡的新增元素的方法
addElement(item);
return item;
}
public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {
//通過記錄modCount引數來實現Fail-Fast機制
modCount++;
//確保棧的容量大小不會使新增的資料溢位
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = obj;
}
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
//防止溢位。超出了陣列可容納的長度,需要進行動態擴充套件!!!
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
//陣列動態增加的關鍵所在
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
//如果是Stack的話,陣列擴充套件為原來的兩倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
//擴充套件陣列後需要判斷兩次
//第1次是新陣列的容量是否比elementCount + 1的小(minCapacity;)
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
//第1次是新陣列的容量是否比指定最大限制Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8 大
//如果大,則minCapacity過大,需要判斷下
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
//檢查容量的int值是不是已經溢位
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
//出棧
public Object pop() throws Exception {
return linkedList.deleteHead();
}
public void display() {
linkedList.display();
}
/** * 棧單鏈表實現:沒有長度限制,並且出棧和入棧速度都很快 */
private class LinkedList {
private class Node {
Node next;
//下一個結點的引用
Object data;
//結點元素
public Node(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
private Node head;
public LinkedList() {
this.head = null;
}
}
public void insertHead(Object data) {
Node node = new Node(data);
node.next = head; head = node;
}
public Object deleteHead() throws Exception {
if (head == null)
throw new Exception("Stack is empty!");
Node temp = head;
//head = temp.next;也行
head = head.next;
return temp.data;
}
public void display() {
if (head == null)
System.out.println("empty");
System.out.print("top -> bottom : | ");
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.data.toString() + " | ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}測試:
@Test
public void testLinkedListStack() {
LinkedListStack lls = new LinkedListStack();
lls.push(1);
lls.push(2);
lls.push(3);
lls.display();
try {
System.out.println(lls.pop());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
lls.display();
}3
top -> bottom : | 2 | 1 |
