JAVA基礎之泛型與集合
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-10
一:泛型:
泛型類的定義格式:
class class-name <type -parma-list>{}
例項化泛型類的格式:
class-name<type-parma-list> obj = new class-name<type-parma-list>(cons-arg-list)
type-parma-list用於指定當前泛型類可接受的型別引數的個數
例子:
泛型類
package com.dh.ch07; public class Generic<T> { private T ob; // 定義泛型成員變數 public Generic(T ob) { this.ob = ob; } public T getOb() { return ob; } public void setOb(T ob) { this.ob = ob; } public void showType() { System.out.println("T實際型別是: " + ob.getClass().getName()); } }
package com.dh.ch07; public class GenericDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // Generic<Integer> obj; // 定義泛型類Genneric的一個Integer版本 Generic<Integer> intOb = new Generic<Integer>(88); intOb.showType(); int i = intOb.getOb(); System.out.println("value= " + i); System.out.println("----------------------------------"); // 定義泛型類Genneric的一個String版本 Generic<String> strOb = new Generic<String>("Hello Gen!"); strOb.showType(); String s = strOb.getOb(); System.out.println("value= " + s); } }
(二)集合:
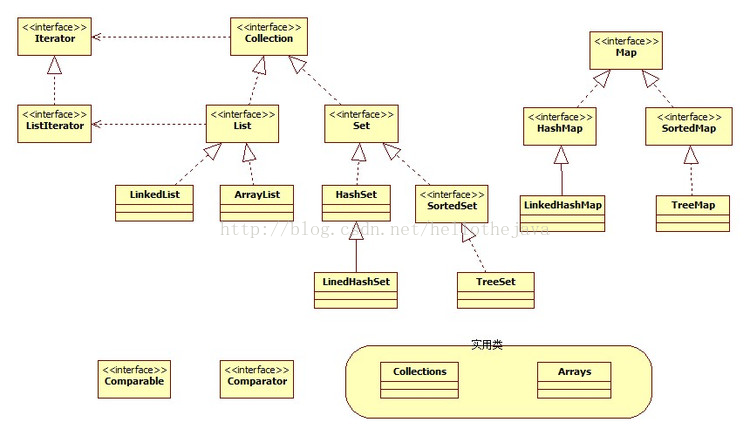
上面是集合的框架。
List介面繼承Collection介面,元素允許重複,一元素的新增順序來放置元素,不會重新排列。
List的實現類有ArrayList和LinkList。
List方法列表我就一一列舉了,打擊可以檢視一下API。
下面舉幾個常用的集合例子:
1.ArrayList和Iterator
import java.util.*; class ArrayListDemo { // public static List<String> arrayList; public static ArrayList<String> arrayList; // 初始化連結串列 public static void init() { arrayList = new ArrayList<String>(4); // 即使生命長度,ArrayList還是根據需要動態分配 System.out.println("初始化長度: " + arrayList.size()); // 新增元素 arrayList.add("first"); arrayList.add("second"); arrayList.add("third"); arrayList.add("forth"); } // 列印連結串列資訊 public static void printInfo() { System.out.println("增加元素後的長度: " + arrayList.size()); // 通過集合構造連結串列 ArrayList<String> arrayList2 = new ArrayList<String>(arrayList); // AbstractCollection對toString()方法提供了實現 System.out.println("arrayList : " + arrayList); System.out.println("arrayList2: " + arrayList2); } // 對連結串列實現修改、刪除操作 public static void modify() { // 新增一個元素 arrayList.add(1, "insert data"); System.out.println("增加元素後的長度: " + arrayList.size()); // 刪除一個元素 arrayList.remove("second"); System.out.println("刪除'second'元素後的長度: " + arrayList.size()); arrayList.remove(2); System.out.println("刪除第3個元素後的長度: " + arrayList.size()); // 刪除一個不存在的元素 arrayList.remove("nothing"); System.out.println("刪除'nothing'元素後的長度: " + arrayList.size()); // 丟擲IndexOutOfBoundsException // arrayList.remove(10); } // 從List中獲取陣列,並遍歷 public static void toArray() { Object[] arr = arrayList.toArray(); for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { String str = (String) arr[i]; System.out.println((i + 1) + " : " + str); } } // 使用Iterator遍歷 public static void travel(){ System.out.println("遍歷前的長度: " + arrayList.size()); // 使用迭代器進行遍歷 Iterator<String> iterator = arrayList.iterator(); int i = 0; while (iterator.hasNext()) { String str = iterator.next(); i++; System.out.println(str); if (i % 3 == 0) { // 通過迭代器刪除元素 iterator.remove(); } } System.out.println("刪除後的長度: " + arrayList.size()); } // 使用for-each遍歷 public static void travel2(){ for(String str:arrayList){ System.out.println(str); } } public static void main(String args[]) { init(); printInfo(); modify(); toArray(); travel(); travel2(); } }
初始化長度: 0
增加元素後的長度: 4
arrayList : [first, second, third, forth]
arrayList2: [first, second, third, forth]
增加元素後的長度: 5
刪除'second'元素後的長度: 4
刪除第3個元素後的長度: 3
刪除'nothing'元素後的長度: 3
1 : first
2 : insert data
3 : forth
遍歷前的長度: 3
first
insert data
forth
刪除後的長度: 2
first
insert dataSet介面:繼承自colletion介面,Set中的元素是不能重複的,其元素新增後不能保證與新增的順序是一致的。
具體的實現類有HashSet和TreeSet
例子:
package com.dh.ch07;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class HashSetDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
HashSet<String> hashSet = new HashSet<String>();
// 新增元素
hashSet.add("first");
hashSet.add("second");
hashSet.add("third");
hashSet.add("forth");
System.out.println(hashSet);
// 遍歷
for(String str: hashSet){
System.out.println(str);
}
}
}
[third, forth, first, second]
third
forth
first
secondpackage com.dh.ch07;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class TreeSetDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
TreeSet<String> treeSet = new TreeSet<String>();
// 新增元素
treeSet.add("first");
treeSet.add("second");
treeSet.add("third");
treeSet.add("forth");
System.out.println(treeSet);
// 遍歷
for(String str: treeSet){
System.out.println(str);
}
}
}
[third, forth, first, second]
third
forth
first
secondTreeSet元素安字串順序排列儲存。
Map介面:實現的類HashMap和TreeMap
Map是一中把鍵物件和值物件進行關聯的容器,Map中的鍵是不允許重複的。
Map中提供了Map.Entry介面,通過Map的Entry方法返回一個實現Map.Entry介面的物件的集合。
例子:
package com.dh.ch07;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
public class HashMapDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// 建立預設HashMap物件
HashMap<String, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
// 新增資料
hashMap.put("Tom", new Integer(23));
hashMap.put("Rose", new Integer(18));
hashMap.put("Jane", new Integer(26));
hashMap.put("Black", new Integer(24));
hashMap.put("Smith", new Integer(21));
// 獲取Entry的集合
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> set = hashMap.entrySet();
// 遍歷所有元素
for (Entry<String, Integer> entry : set) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " : " + entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println("---------");
// 獲取鍵集
Set<String> keySet = hashMap.keySet();
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer("");
for (String str : keySet) {
buffer.append(str + ",");
}
String str = buffer.substring(0, buffer.length() - 1);
System.out.println(str);
}
}
Tom : 23
Smith : 21
Rose : 18
Black : 24
Jane : 26
---------
Tom,Smith,Rose,Black,Jane下一篇是關於JDBC