杭電1022——Train Problem I(棧的應用)
Problem Description
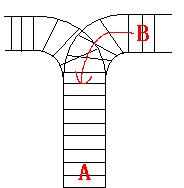
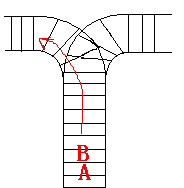
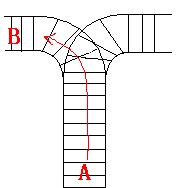
As the new term comes, the Ignatius Train Station is very busy nowadays. A lot of student want to get back to school by train(because the trains in the Ignatius Train Station is the fastest all over the world ^v^). But here comes a problem, there is only one railway where all the trains stop. So all the trains come in from one side and get out from the other side. For this problem, if train A gets into the railway first, and then train B gets into the railway before train A leaves, train A can’t leave until train B leaves. The pictures below figure out the problem. Now the problem for you is, there are at most 9 trains in the station, all the trains has an ID(numbered from 1 to n), the trains get into the railway in an order O1, your task is to determine whether the trains can get out in an order O2.
Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test case consists of an integer, the number of trains, and two strings, the order of the trains come in:O1, and the order of the trains leave:O2. The input is terminated by the end of file. More details in the Sample Input.
Output
The output contains a string “No.” if you can’t exchange O2 to O1, or you should output a line contains “Yes.”, and then output your way in exchanging the order(you should output “in” for a train getting into the railway, and “out” for a train getting out of the railway). Print a line contains “FINISH” after each test case. More details in the Sample Output.
Sample Input
3 123 321
3 123 312
Sample Output
Yes.
in
in
in
out
out
out
FINISH
No.
FINISH
Hint
Hint
For the first Sample Input, we let train 1 get in, then train 2 and train 3.
So now train 3 is at the top of the railway, so train 3 can leave first, then train 2 and train 1.
In the second Sample input, we should let train 3 leave first, so we have to let train 1 get in, then train 2 and train 3.
Now we can let train 3 leave.
But after that we can’t let train 1 leave before train 2, because train 2 is at the top of the railway at the moment.
So we output “No.”.
主要演算法:
掃描字串2。如果當前字元與棧頂元素相等,則出棧,並且掃描字串2中下一個字元;如果棧為空或者字串2中掃描的當前字元與棧頂元素不相等,則字串1中字元按順序壓入棧中,直到滿足字串2當前掃描字元和棧頂字元相等。再次,棧頂元素出棧,並且掃描字串2中下一個字元。如此重複下去,如果最終棧為空,則輸出Yes.如果棧頂元素和字串2中當前掃描的字元不等,且字串1中的元素已經全部進棧,則輸出No.
注意:每個case完了之後要清空棧。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#define MAX 50
typedef struct{
char data[MAX];
int top;
}Stack;
void Initial(Stack *s);
char getTop(Stack *s);
int Push(Stack *s,char ch);
int Pop(Stack *s);
int main()
{
int n;
char s1[MAX],s2[MAX];
char in_out[MAX][5];
Stack s;
Initial(&s);
while(scanf("%d%s%s",&n,s1,s2)!=EOF)
{
int i=0,j=0,k=0,flag=1;
memset(in_out,0,MAX*5*sizeof(char));
Push(&s,s1[i++]);
strcpy(in_out[k++],"in");
while(i<n||j<n)
{
while(s.top==0||s2[j]!=getTop(&s))
{
if(i<n)
{
Push(&s,s1[i++]);
strcpy(in_out[k++],"in");
}
else
{
flag=0;
break;
}
}
if(flag==0)
break;
Pop(&s);
strcpy(in_out[k++],"out");
j++;
}
if(s.top==0)
{
printf("Yes.\n");
for(i=0;i<k;i++)
printf("%s\n",in_out[i]);
printf("FINISH\n");
}
else
{
printf("No.\nFINISH\n");
}
s.top=0;//注意要將棧清空
}
return 0;
}
void Initial(Stack *s)
{
s->top=0;
}
char getTop(Stack *s)
{
return s->data[s->top-1];
}
int Push(Stack *s,char ch)
{
if(s->top>=MAX)
return 0;
else
{
s->data[s->top++]=ch;
return 1;
}
}
int Pop(Stack *s)
{
if(s->top>=MAX)
return 0;
else
{
s->data[--s->top]=0;
return 1;
}
}