ID3決策樹演算法原理及C++實現(其中程式碼轉自別人的部落格)
分類是資料探勘中十分重要的組成部分.
分類作為一種無監督學習方式被廣泛的使用.
之前關於"資料探勘中十大經典演算法"中,基於ID3核心思想的分類演算法
C4.5榜上有名.所以不難看出ID3在資料分類中是多麼的重要了.
ID3又稱為決策樹演算法,雖然現在廣義的決策樹演算法不止ID3一種,但是由
於ID3的重要性,習慣是還是把ID3和決策樹演算法等價起來.
另外無監督學習方式我還要多說兩句.無監督學習方式包括決策樹演算法,
基於規則的分類,神經網路等.這些分類方式是初始分類已知,將樣本分為
訓練樣本和測試樣本,訓練樣本用於根據特定的輸入輸出關係訓練出特定
的分類對映關係.然後通過此對映關係將測試樣本對映到相應的類別上.
先讓大家對決策樹演算法有個直觀的印象.
例如下:
套用俗語,決策樹分類的思想類似於找物件。現想象一個女孩的母親要給這個女孩介紹男朋友,於是有了下面的對話:
女兒:多大年紀了?
母親:26。
女兒:長的帥不帥?
母親:挺帥的。
女兒:收入高不?
母親:不算很高,中等情況。
女兒:是公務員不?
母親:是,在稅務局上班呢。
女兒:那好,我去見見。
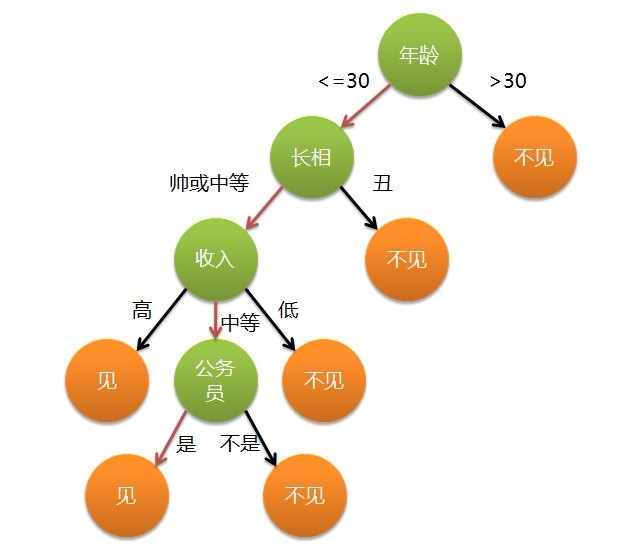
這個女孩的決策過程就是典型的分類樹決策。相當於通過年齡、長相、收入和是否公務員對將男人分為兩個類別:見和不見。假設這個女孩對男人的要求是:30歲以下、長相中等以上並且是高收入者或中等以上收入的公務員,那麼這個可以用下圖表示女孩的決策邏輯:
不難看出女兒選老公是通過一個一個條件逐步決策的.這些條件包括年齡,長相,收入,是否公務員.而如何選取
圖-1
這些條件的優先順序呢,意思是女兒選老公的條件是如何排序的呢,顯然首先考慮的是年齡.其次是長相.再次是
收入,最後才是是不是公務員.如何說一個男人的年齡超過了30歲那麼一開始就被排除在外了.
那麼我們如何確定這些條件的優先順序,所以這就是決策樹演算法必須的一個過程-----訓練
通過已知的樣本來確定條件屬性在決策中的優先順序,進而達到樣本目標分類的結果.
那麼這個條件屬性的優先順序到底是如何定量的呢?所以這裡不得不提到的一個概念就是資訊熵.
資訊熵是度量資料中包含的資訊,概率的度量.資訊熵是資訊理論中的概念,可以這樣理解.變數的不
確定性越大,資訊熵越大.一組資料越有序,其包含的資訊量越小,資訊熵越小.一組資料越無序,越
混亂,其包含的資訊量越大,資訊熵越大
比如一組資料{x1,x2,x3.....xn};其和是sum,那麼這組資料的資訊熵
H(X)=-∑(x1/sum)*log(x1/sum);
而決策樹演算法中訓練樣本就是通過計算資訊增益來決定條件屬性的優先權的.
下面我還是用一個例子來說明如何通過資訊熵來選取條件屬性的決策優先權.
通過上面訓練出來的決策樹我們不難得到下面這樣一個訓練前的表格:
| 年齡 | 長相 | 收入 | 公務員 | 見/不見 |
| >30 | 醜 | 低 | 是 | 不見 |
| <=30 | 醜 | 高 | 不是 | 不見 |
| <=30 | 帥或中等 | 低 | 不是 | 不見 |
| <=30 | 帥或中等 | 高 | 是 | 見 |
| <=30 | 帥或中等 | 中等 | 是 | 見 |
| <=30 | 帥或中等 | 中等 | 不是 | 不見 |
表中紅色字型部分為補充部分,即表示對生成決策樹沒有影響,可以隨意填.
那麼現在上面表格共有五個屬性列,其中前四列(年齡,長相,收入,公務員)為條件屬性,而最後一列為目標屬性.
我們的目的是通過條件屬性的資訊熵來得出資訊熵的優先順序,進而推出之前圖-1的決策樹.
首先計算出目標屬性--見/不見的資訊熵.見/不見屬性有兩種取值情況:見,不見.其中見有兩次,不見有四次.
那麼目標屬性的資訊熵為:H(D)=-(2/6)*log(2/6)-(4/6)*log(4/6)=0.639;(log取e為底)
接下來求各個條件屬性取不同值熵(以年齡為例):
H(年齡>30)=0;
H(年齡<=30)=-(3/5)log(3/5)-(2/5)log(2/5)=0.672;
接下來求年齡屬性的資訊熵:H(年齡)=-(1/6)*0-(5/6)*0.672=0.558;
類似的求出長相屬性的資訊熵:H(長相)=0.457
類似的求出收入屬性的資訊熵:H(收入)=0.457
類似的求出是否公務員的資訊熵:H(公務員)=0.318
下面引入資訊增益(information gain)這個概念,用Gain(D)表示,
該概念是指資訊熵的有效減少量,該量越高,表明目標屬性在該參考屬性那失去的資訊熵越多,
那麼該屬性越應該在決策樹的上層.
所以Gain(年齡)=H(D)-H(年齡)=0.114
Gain(長相)=H(D)-H(長相)=0.215
Gain(收入)=H(D)-H(年齡)=0.215
Gain(公務員=H(D)-H(公務員)=0.354
所以先按照條件屬性年齡將資料分為:
| 年齡 | 長相 | 收入 | 公務員 | 見/不見 |
| >30 | 醜 | 低 | 是 | 不見 |
| 年齡 | 長相 | 收入 | 公務員 | 見/不見 |
| <=30 | 醜 | 高 | 不是 | 不見 |
| <=30 | 帥或中等 | 低 | 不是 | 不見 |
| <=30 | 帥或中等 | 高 | 是 | 見 |
| <=30 | 帥或中等 | 中等 | 是 | 見 |
| <=30 | 帥或中等 | 中等 | 不是 | 不見 |
對錶3還是按上述方式計算資訊熵,再進行決策分類.只不過,這時候不考慮表三的年齡屬性.
一直這樣遞迴,直到當分到某類時目標屬性全是一個值的時候,這時候.由訓練樣本訓練的
決策樹或者說決策樹規則就產生了.接下來對需要分類的資料運用此決策樹規則分類即可.
程式碼太長了,每時間讀,轉載過來大家共享.
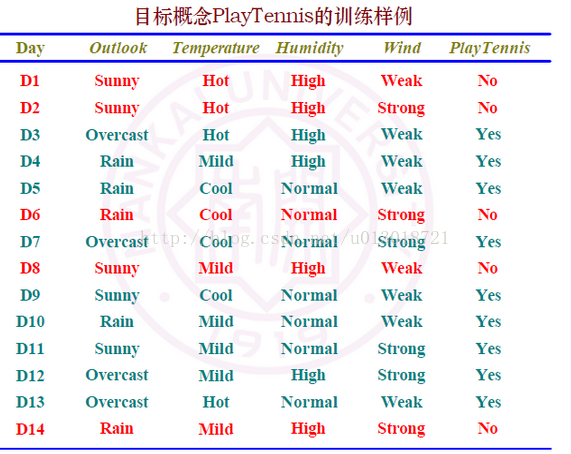
下表為訓練樣本資料:
C++原始碼如下所示:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <math.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
#define ROW 14
#define COL 5
#define log2 0.69314718055
typedef struct TNode
{
char data[15];
char weight[15];
TNode * firstchild,*nextsibling;
}*tree;
typedef struct LNode
{
char OutLook[15];
char Temperature[15];
char Humidity[15];
char Wind[15];
char PlayTennis[5];
LNode *next;
}*link;
typedef struct AttrNode
{
char attributes[15];//屬性
int attr_Num;//屬性的個數
AttrNode *next;
}*Attributes;
char * Examples[ROW][COL] = {//"OverCast","Cool","High","Strong","No",
// "Rain","Hot","Normal","Strong","Yes",
"Sunny","Hot","High","Weak","No",
"Sunny","Hot","High","Strong","No",
"OverCast","Hot","High","Weak","Yes",
"Rain","Mild","High","Weak","Yes",
"Rain","Cool","Normal","Weak","Yes",
"Rain","Cool","Normal","Strong","No",
"OverCast","Cool","Normal","Strong","Yes",
"Sunny","Mild","High","Weak","No",
"Sunny","Cool","Normal","Weak","Yes",
"Rain","Mild","Normal","Weak","Yes",
"Sunny","Mild","Normal","Strong","Yes",
"OverCast","Mild","Normal","Strong","Yes",
"OverCast","Hot","Normal","Weak","Yes",
"Rain","Mild","High","Strong","No"
};
char * Attributes_kind[4] = {"OutLook","Temperature","Humidity","Wind"};
int Attr_kind[4] = {3,3,2,2};
char * OutLook_kind[3] = {"Sunny","OverCast","Rain"};
char * Temperature_kind[3] = {"Hot","Mild","Cool"};
char * Humidity_kind[2] = {"High","Normal"};
char * Wind_kind[2] = {"Weak","Strong"};
/*int i_Exampple[14][5] = {0,0,0,0,1,
0,0,0,1,1,
1,0,0,1,0,
2,1,0,0,0,
2,2,1,0,0,
2,2,1,1,1,
1,2,1,1,0,
0,1,0,0,1,
0,2,1,0,0,
2,1,1,0,0,
0,1,1,1,0,
1,1,1,1,0,
1,1,1,0,0,
2,1,0,0,1
};*/
void treelists(tree T);
void InitAttr(Attributes &attr_link,char * Attributes_kind[],int Attr_kind[]);
void InitLink(link &L,char * Examples[][COL]);
void ID3(tree &T,link L,link Target_Attr,Attributes attr);
void PN_Num(link L,int &positve,int &negative);
double Gain(int positive,int negative,char * atrribute,link L,Attributes attr_L);
void main()
{
link LL,p;
Attributes attr_L,q;
tree T;
T = new TNode;
T->firstchild = T->nextsibling = NULL;
strcpy(T->weight,"");
strcpy(T->data,"");
attr_L = new AttrNode;
attr_L->next = NULL;
LL = new LNode;
LL->next = NULL;
//成功建立兩個連結串列
InitLink(LL,Examples);
InitAttr(attr_L,Attributes_kind,Attr_kind);
ID3(T,LL,NULL,attr_L);
cout<<"決策樹以廣義表形式輸出如下:"<<endl;
treelists(T);//以廣義表的形式輸出樹
// cout<<Gain(9,5,"OutLook",LL,attr_L)<<endl;
cout<<endl;
}
//以廣義表的形式輸出樹
void treelists(tree T)
{
tree p;
if(!T)
return;
cout<<"{"<<T->weight<<"}";
cout<<T->data;
p = T->firstchild;
if (p)
{
cout<<"(";
while (p)
{
treelists(p);
p = p->nextsibling;
if (p)cout<<',';
}
cout<<")";
}
}
void InitAttr(Attributes &attr_link,char * Attributes_kind[],int Attr_kind[])
{
Attributes p;
for (int i =0;i < 4;i++)
{
p = new AttrNode;
p->next = NULL;
strcpy(p->attributes,Attributes_kind[i]);
p->attr_Num = Attr_kind[i];
p->next = attr_link->next;
attr_link->next = p;
}
}
void InitLink(link &LL,char * Examples[][COL])
{
link p;
for (int i = 0;i < ROW;i++)
{
p = new LNode;
p->next = NULL;
strcpy(p->OutLook,Examples[i][0]);
strcpy(p->Temperature,Examples[i][1]);
strcpy(p->Humidity,Examples[i][2]);
strcpy(p->Wind,Examples[i][3]);
strcpy(p->PlayTennis,Examples[i][4]);
p->next = LL->next;
LL->next = p;
}
}
void PN_Num(link L,int &positve,int &negative)
{
positve = 0;
negative = 0;
link p;
p = L->next;
while (p)
{
if (strcmp(p->PlayTennis,"No") == 0)
negative++;
else if(strcmp(p->PlayTennis,"Yes") == 0)
positve++;
p = p->next;
}
}
//計算資訊增益
//link L: 樣本集合S
//attr_L:屬性集合
double Gain(int positive,int negative,char * atrribute,link L,Attributes attr_L)
{
int atrr_kinds;//每個屬性中的值的個數
Attributes p = attr_L->next;
link q = L->next;
int attr_th = 0;//第幾個屬性
while (p)
{
if (strcmp(p->attributes,atrribute) == 0)
{
atrr_kinds = p->attr_Num;
break;
}
p = p->next;
attr_th++;
}
double entropy,gain=0;
double p1 = 1.0*positive/(positive + negative);
double p2 = 1.0*negative/(positive + negative);
entropy = -p1*log(p1)/log2 - p2*log(p2)/log2;//集合熵
gain = entropy;
//獲取每個屬性值在訓練樣本中出現的個數
//獲取每個屬性值所對應的正例和反例的個數
//宣告一個3*atrr_kinds的陣列
int ** kinds= new int * [3];
for (int j =0;j < 3;j++)
{
kinds[j] = new int[atrr_kinds];//儲存每個屬性值在訓練樣本中出現的個數
}
//初始化
for (j = 0;j< 3;j++)
{
for (int i =0;i < atrr_kinds;i++)
{
kinds[j][i] = 0;
}
}
while (q)
{
if (strcmp("OutLook",atrribute) == 0)
{
for (int i = 0;i < atrr_kinds;i++)
{
if(strcmp(q->OutLook,OutLook_kind[i]) == 0)
{
kinds[0][i]++;
if(strcmp(q->PlayTennis,"Yes") == 0)
kinds[1][i]++;
else
kinds[2][i]++;
}
}
}
else if (strcmp("Temperature",atrribute) == 0)
{
for (int i = 0;i < atrr_kinds;i++)
{
if(strcmp(q->Temperature,Temperature_kind[i]) == 0)
{
kinds[0][i]++;
if(strcmp(q->PlayTennis,"Yes") == 0)
kinds[1][i]++;
else
kinds[2][i]++;
}
}
}
else if (strcmp("Humidity",atrribute) == 0)
{
for (int i = 0;i < atrr_kinds;i++)
{
if(strcmp(q->Humidity,Humidity_kind[i]) == 0)
{
kinds[0][i]++;
if(strcmp(q->PlayTennis,"Yes") == 0)
kinds[1][i]++;//
else
kinds[2][i]++;
}
}
}
else if (strcmp("Wind",atrribute) == 0)
{
for (int i = 0;i < atrr_kinds;i++)
{
if(strcmp(q->Wind,Wind_kind[i]) == 0)
{
kinds[0][i]++;
if(strcmp(q->PlayTennis,"Yes") == 0)
kinds[1][i]++;
else
kinds[2][i]++;
}
}
}
q = q->next;
}
//計算資訊增益
double * gain_kind = new double[atrr_kinds];
int positive_kind = 0,negative_kind = 0;
for (j = 0;j < atrr_kinds;j++)
{
if (kinds[0][j] != 0 && kinds[1][j] != 0 && kinds[2][j] != 0)
{
p1 = 1.0*kinds[1][j]/kinds[0][j];
p2 = 1.0*kinds[2][j]/kinds[0][j];
gain_kind[j] = -p1*log(p1)/log2-p2*log(p2)/log2;
gain = gain - (1.0*kinds[0][j]/(positive + negative))*gain_kind[j];
}
else
gain_kind[j] = 0;
}
return gain;
}
//在ID3演算法中的訓練樣本子集合與屬性子集合的連結串列需要進行清空
void FreeLink(link &Link)
{
link p,q;
p = Link->next;
Link->next = NULL;
while (p)
{
q = p;
p = p->next;
free(q);
}
}
void ID3(tree &T,link L,link Target_Attr,Attributes attr)
{
Attributes p,max,attr_child,p1;
link q,link_child,q1;
tree r,tree_p;
int positive =0,negative =0;
PN_Num(L,positive,negative);
//初始化兩個子集合
attr_child = new AttrNode;
attr_child->next = NULL;
link_child = new LNode;
link_child->next = NULL;
if (positive == 0)//全是反例
{
strcpy(T->data,"No");
return;
}
else if( negative == 0)//全是正例
{
strcpy(T->data,"Yes");
return;
}
p = attr->next; //屬性連結串列
double gain,g = 0;
/************************************************************************/
/* 建立屬性子集合與訓練樣本子集合有兩個方案:
一:在原來連結串列的基礎上進行刪除;
二:另外申請空間進行儲存子集合;
採用第二種方法雖然浪費了空間,但也省了很多事情,避免了變數之間的應用混亂
*/
/************************************************************************/
if(p)
{
while (p)
{
gain = Gain(positive,negative,p->attributes,L,attr);
cout<<p->attributes<<" "<<gain<<endl;
if(gain > g)
{
g = gain;
max = p;//尋找資訊增益最大的屬性
}
p = p->next;
}
strcpy(T->data,max->attributes);//增加決策樹的節點
cout<<"資訊增益最大的屬性:max->attributes = "<<max->attributes<<endl<<endl;
//下面開始建立決策樹
//建立屬性子集合
p = attr->next;
while (p)
{
if (strcmp(p->attributes,max->attributes) != 0)
{
p1 = new AttrNode;
strcpy(p1->attributes,p->attributes);
p1->attr_Num = p->attr_Num;
p1->next = NULL;
p1->next = attr_child->next;
attr_child->next = p1;
}
p = p->next;
}
//需要區分出是哪一種屬性
//建立每一層的第一個節點
if (strcmp("OutLook",max->attributes) == 0)
{
r = new TNode;
r->firstchild = r->nextsibling = NULL;
strcpy(r->weight,OutLook_kind[0]);
T->firstchild = r;
//獲取與屬性值相關的訓練樣例Example(vi),建立一個新的訓練樣本連結串列link_child
q = L->next;
while (q)
{
if (strcmp(q->OutLook,OutLook_kind[0]) == 0)
{
q1 = new LNode;
strcpy(q1->OutLook,q->OutLook);
strcpy(q1->Humidity,q->Humidity);
strcpy(q1->Temperature,q->Temperature);
strcpy(q1->Wind,q->Wind);
strcpy(q1->PlayTennis,q->PlayTennis);
q1->next = NULL;
q1->next = link_child->next;
link_child->next = q1;
}
q = q->next;
}
}
else if (strcmp("Temperature",max->attributes) == 0)
{
r = new TNode;
r->firstchild = r->nextsibling = NULL;
strcpy(r->weight,Temperature_kind[0]);
T->firstchild = r;
//獲取與屬性值相關的訓練樣例Example(vi),建立一個新的訓練樣本連結串列link_child
q = L->next;
while (q)
{
if (strcmp(q->Temperature,Temperature_kind[0]) == 0)
{
q1 = new LNode;
strcpy(q1->OutLook,q->OutLook);
strcpy(q1->Humidity,q->Humidity);
strcpy(q1->Temperature,q->Temperature);
strcpy(q1->Wind,q->Wind);
strcpy(q1->PlayTennis,q->PlayTennis);
q1->next = NULL;
q1->next = link_child->next;
link_child->next = q1;
}
q = q->next;
}
}
else if (strcmp("Humidity",max->attributes) == 0)
{
r = new TNode;
r->firstchild = r->nextsibling = NULL;
strcpy(r->weight,Humidity_kind[0]);
T->firstchild = r;
//獲取與屬性值相關的訓練樣例Example(vi),建立一個新的訓練樣本連結串列link_child
q = L->next;
while (q)
{
if (strcmp(q->Humidity,Humidity_kind[0]) == 0)
{
q1 = new LNode;
strcpy(q1->OutLook,q->OutLook);
strcpy(q1->Humidity,q->Humidity);
strcpy(q1->Temperature,q->Temperature);
strcpy(q1->Wind,q->Wind);
strcpy(q1->PlayTennis,q->PlayTennis);
q1->next = NULL;
q1->next = link_child->next;
link_child->next = q1;
}
q = q->next;
}
}
else if (strcmp("Wind",max->attributes) == 0)
{
r = new TNode;
r->firstchild = r->nextsibling = NULL;
strcpy(r->weight,Wind_kind[0]);
T->firstchild = r;
//獲取與屬性值相關的訓練樣例Example(vi),建立一個新的訓練樣本連結串列link_child
q = L->next;
while (q)
{
if (strcmp(q->Wind,Wind_kind[0]) == 0)
{
q1 = new LNode;
strcpy(q1->OutLook,q->OutLook);
strcpy(q1->Humidity,q->Humidity);
strcpy(q1->Temperature,q->Temperature);
strcpy(q1->Wind,q->Wind);
strcpy(q1->PlayTennis,q->PlayTennis);
q1->next = NULL;
q1->next = link_child->next;
link_child->next = q1;
}
q = q->next;
}
}
int p = 0,n = 0;
PN_Num(link_child,p,n);
if (p != 0 && n != 0)
{
ID3(T->firstchild,link_child,Target_Attr,attr_child);
FreeLink(link_child);
}
else if(p == 0)
{
strcpy(T->firstchild->data,"No");
FreeLink(link_child);
// strcpy(T->firstchild->data,q1->PlayTennis);//----此處應該需要修改----:)
}
else if(n == 0)
{
strcpy(T->firstchild->data,"Yes");
FreeLink(link_child);
}
//建立每一層上的其他節點
tree_p = T->firstchild;
for (int i = 1;i < max->attr_Num;i++)
{
//需要區分出是哪一種屬性
if (strcmp("OutLook",max->attributes) == 0)
{
r = new TNode;
r->firstchild = r->nextsibling = NULL;
strcpy(r->weight,OutLook_kind[i]);
tree_p->nextsibling = r;
//獲取與屬性值相關的訓練樣例Example(vi),建立一個新的訓練樣本連結串列link_child
q = L->next;
while (q)
{
if (strcmp(q->OutLook,OutLook_kind[i]) == 0)
{
q1 = new LNode;
strcpy(q1->OutLook,q->OutLook);
strcpy(q1->Humidity,q->Humidity);
strcpy(q1->Temperature,q->Temperature);
strcpy(q1->Wind,q->Wind);
strcpy(q1->PlayTennis,q->PlayTennis);
q1->next = NULL;
q1->next = link_child->next;
link_child->next = q1;
}
q = q->next;
}
}
else if (strcmp("Temperature",max->attributes) == 0)
{
r = new TNode;
r->firstchild = r->nextsibling = NULL;
strcpy(r->weight,Temperature_kind[i]);
tree_p->nextsibling = r;
//獲取與屬性值相關的訓練樣例Example(vi),建立一個新的訓練樣本連結串列link_child
q = L->next;
while (q)
{
if (strcmp(q->Temperature,Temperature_kind[i]) == 0)
{
q1 = new LNode;
strcpy(q1->OutLook,q->OutLook);
strcpy(q1->Humidity,q->Humidity);
strcpy(q1->Temperature,q->Temperature);
strcpy(q1->Wind,q->Wind);
strcpy(q1->PlayTennis,q->PlayTennis);
q1->next = NULL;
q1->next = link_child->next;
link_child->next = q1;
}
q = q->next;
}
}
else if (strcmp("Humidity",max->attributes) == 0)
{
r = new TNode;
r->firstchild = r->nextsibling = NULL;
strcpy(r->weight,Humidity_kind[i]);
tree_p->nextsibling = r;
//獲取與屬性值相關的訓練樣例Example(vi),建立一個新的訓練樣本連結串列link_child
q = L->next;
while (q)
{
if (strcmp(q->Humidity,Humidity_kind[i]) == 0)
{
q1 = new LNode;
strcpy(q1->OutLook,q->OutLook);
strcpy(q1->Humidity,q->Humidity);
strcpy(q1->Temperature,q->Temperature);
strcpy(q1->Wind,q->Wind);
strcpy(q1->PlayTennis,q->PlayTennis);
q1->next = NULL;
q1->next = link_child->next;
link_child->next = q1;
}
q = q->next;
}
}
else if (strcmp("Wind",max->attributes) == 0)
{
r = new TNode;
r->firstchild = r->nextsibling = NULL;
strcpy(r->weight,Wind_kind[i]);
tree_p->nextsibling = r;
//獲取與屬性值相關的訓練樣例Example(vi),建立一個新的訓練樣本連結串列link_child
q = L->next;
while (q)
{
if (strcmp(q->Wind,Wind_kind[i]) == 0)
{
q1 = new LNode;
strcpy(q1->OutLook,q->OutLook);
strcpy(q1->Humidity,q->Humidity);
strcpy(q1->Temperature,q->Temperature);
strcpy(q1->Wind,q->Wind);
strcpy(q1->PlayTennis,q->PlayTennis);
q1->next = NULL;
q1->next = link_child->next;
link_child->next = q1;
}
q = q->next;
}
}
int p = 0,n = 0;
PN_Num(link_child,p,n);
if (p != 0 && n != 0)
{
ID3(tree_p->nextsibling,link_child,Target_Attr,attr_child);
FreeLink(link_child);
}
else if(p == 0)
{
strcpy(tree_p->nextsibling->data,"No");
FreeLink(link_child);
}
else if(n == 0)
{
strcpy(tree_p->nextsibling->data,"Yes");
FreeLink(link_child);
}
tree_p = tree_p->nextsibling;//建立所有的孩子結點
}//建立決策樹結束
}
else
{
q = L->next;
strcpy(T->data,q->PlayTennis);
return;//這個地方要賦以訓練樣本Example中最普遍的Target_attributes的值
}
}
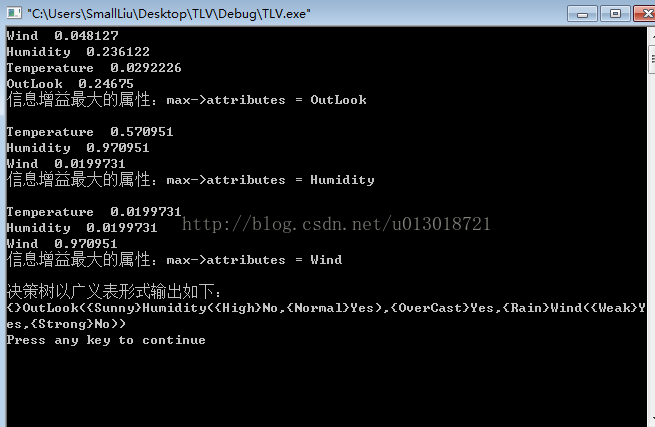
執行結果如下:
轉載請註明作者:小劉