雙向連結串列結構衍生出來的LRU快取(來自leetcode題目)
import java.util.HashMap;
/*
Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache. It should support the following operations: get and put.
get(key) - Get the value (will always be positive) of the key if the key exists in the cache, otherwise return -1.
put(key, value) - Set or insert the value if the key is not already present. When the cache reached its capacity, it should invalidate the least recently used item before inserting a new item.
Follow up:
Could you do both operations in O(1) time complexity?
LRUCache cache = new LRUCache(2);
cache.put(1, 1);
cache.put(2, 2);
cache.get(1); // returns 1
cache.put(3, 3); // evicts key 2
cache.get(2); // returns -1 (not found)
cache.put(4, 4); // evicts key 1
cache.get(1); // returns -1 (not found)
cache.get(3); // returns 3
cache.get(4); // returns 4
*/
class Node{//雙向連結串列
int key;
int value;
Node next;
Node pre;
public Node(int key,int value,Node pre, Node next){
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.pre = pre;
this.next = next;
}
}
public class LRUCache {
int capacity;
int count;//cache size
Node head;
Node tail;
HashMap<Integer,Node>hm;
public LRUCache(int capacity) { //only initial 2 Node is enough, head/tail
this.capacity = capacity;
this.count = 2;
this.head = new Node(-1,-1,null,null);
this.tail = new Node(-2,-2,this.head,null);
this.head.next = this.tail;
hm = new HashMap<Integer,Node>();
hm.put(this.head.key, this.head);
hm.put(this.tail.key, this.tail);
}
public int get(int key) {
int value = -1;
if(hm.containsKey(key)){
Node nd = hm.get(key);
value = nd.value;
detachNode(nd); //detach nd from current place
insertToHead(nd); //insert nd into head
}
return value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if(hm.containsKey(key)){ //update
Node nd = hm.get(key);
nd.value = value;
//move to head
detachNode(nd); //detach nd from current place
insertToHead(nd); //insert nd into head
}else{ //add
Node newNd = new Node(key,value,null,this.head);
this.head.pre = newNd; //insert into head
this.head = newNd;
hm.put(key, newNd); //add into hashMap
this.count ++;
if(this.count > capacity){ //need delete node
removeNode();
}
}
}
//common func
public void insertToHead(Node nd){//最後結果為B->C->A
//A->C->B,當前節點為C,頭節點為A
//頭節點的前一節點插入...........
this.head.pre = nd;
nd.next = this.head;
nd.pre = null;
this.head = nd;
}
public void detachNode(Node nd){
//當前節點為nd,頭節點為head
//比如 A->B->C,頭節點為A,當前節點為B
//當前節點的前一節點指向當前節點的下一節點 A->C
nd.pre.next = nd.next;
if(nd.next!=null){
//若當前節點的下一節點存在,則當前節點的下一節點的前一節點為當前節點的前一節點
nd.next.pre = nd.pre;
//否則,尾節點為當前節點的前一節點,即A->C->B
}else{
this.tail = nd.pre;
}
}
public void removeNode(){ //remove from tail
int tailKey = this.tail.key;
this.tail = this.tail.pre;
this.tail.next = null;
hm.remove(tailKey);
this.count --;
}
public void printCache(){
System.out.println("\nPRINT CACHE ------ ");
System.out.println("count: "+count);
System.out.println("From head:");
Node p = this.head;
while(p!=null){
System.out.println("key: "+p.key+" value: "+p.value);
p = p.next;
}
System.out.println("From tail:");
p = this.tail;
while(p!=null){
System.out.println("key: "+p.key+" value: "+p.value);
p = p.pre;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
LRUCache lc = new LRUCache(3);
System.out.println("LRUCache初始化狀態,Cache初始容量是2");
lc.printCache();
lc.put(1, 1);
lc.put(2, 2);
lc.put(3, 3);
System.out.println("第一次put操作後的結果");
lc.printCache();
lc.get(2);
System.out.println("第一次get(key==2)操作後的結果");
lc.printCache();
lc.put(4, 4);
System.out.println("第二次put(key==4)操作後的結果,容量已滿,替換最不常用的key和value");
lc.printCache();
lc.get(1);
System.out.println("第二次get(key==1)操作後的結果");
lc.printCache();
lc.put(3, 33);
System.out.println("第三次put(key==3)操作後的結果,替換已有key的值");
lc.printCache();
}
}
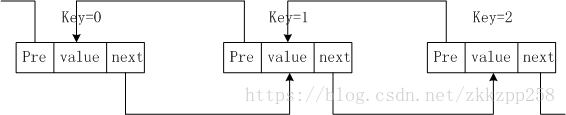
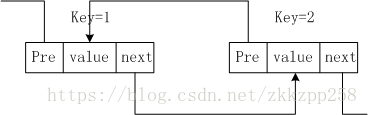
雙向連結串列:
class Node{
int key;
int value;
Node next;//下一節點
Node pre;//前一節點
public Node(int key,int value,Node pre, Node next){
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.pre = pre;
this.next = next;
}
}
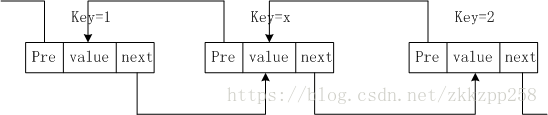
圖解結構如下,
插入:假設要在key=1和key=2之間插入一個節點key=x
則,
Node k1,k2,kx;
已知k2,kx
kx.next = k2;
kx.pre = k2.pre;
k2.pre.next = kx;
----------------------------------
private Node head = new Node(null);
private void addBefore(Node newNode, Node node){
newNode.next = node;
newNode.pre = node.pre;
Node.pre.next = newNode;
}
單鏈表的反轉:
static ListNode reverseLinkedList(ListNode node) {
ListNode previousNode = null;
ListNode currentNode = node;
ListNode headNode = null;
while (currentNode != null) {
ListNode nextNode = currentNode.next;
if (nextNode == null) {
headNode = currentNode;
}
currentNode.next = previousNode;
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = nextNode;
}
return headNode;
}
雙向連結串列操作可以參看LinkedList類中的構造方法(增刪查詢):
相關推薦
雙向連結串列結構衍生出來的LRU快取(來自leetcode題目)
import java.util.HashMap; /* Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache. It should support the following
算法系列-連結串列:如何實現LRU快取淘汰演算法
整理自極客時間-資料結構與演算法之美。原文內容更完整具體,且有音訊。購買地址: 開篇語 今天我們來聊聊“連結串列(Linked list)經典的應用場景,那就是 LRU 快取淘汰演算法。 快取是一種提高資料讀取效能的技術,在硬體設計、軟體開發中都有著非常廣泛的應用,
資料結構學習之雙向連結串列結構
注:本文的主要目的是為了記錄自己的學習過程,也方便與大家做交流。轉載請註明來自: 在前面總結的單向連結串列結構的基礎上,現在開始著手實踐實踐雙向連結串列結構,如果充分理解了單向連結串列資料結構,那對雙向連結串列結構的理解也就不再困難,換個角度而言,雙向連
leetcode 刪除連結串列倒數第n個節點(一次掃描)
題目描述 給定一個連結串列,刪除連結串列的倒數第 n 個節點,並且返回連結串列的頭結點。 演算法思想 採用一次掃描的辦法,需要定位到刪除節點的前面的節點 因此指標p往後挪動的個數為n+1次 注意如果p挪動之後,碰到空,說明刪除的是頭結點 使用兩個指標,一個從頭還是挪動,一
LRU快取策略(雙向連結串列實現)
雙向連結串列實現LRU Cache注意1.各種邊界條件(改節點位置的時候考慮節點目前的位置) 2.查詢到,插入(分update,set)都要考慮找到元素的位置的修改。複雜度get,set為O(n)public class LRUCache { int ca
雙向連結串列簡單實現--資料結構與演算法紀錄片第一記
從這個月開始得準備春招的東西,所以打算重新學習資料結構與演算法,以後的部落格就以這個為主。 今天是線性結構中的雙向連結串列。 程式碼實現與測試: DoubleLinkNode: package linear.doublelink;/** * @Description: 連結串列節點結
雙向連結串列實現的LRU演算法
LRU是Least Recently Used的縮寫,即最近最少使用頁面置換演算法,是為虛擬頁式儲存管理服務的,是根據頁面調入記憶體後的使用情況進行決策了。由於無法預測各頁面將來的使用情況,只能利用“最近的過去”作為“最近的將來”的近似
js資料結構 -- 連結串列, 雙向連結串列,迴圈連結串列
陣列作為js常用的資料結構,存取元素都非常的方便,但是其內部的實現原理跟其他計算機語言對陣列的實現都是一樣的。 由於陣列在記憶體中的儲存是連續的,所以當在陣列的開頭或者中間插入元素時,內部都需要去移動其他元素的位置,這個移動元素的成本很高。 連結串列也是儲存有序的元素集合,但不同
資料結構與演算法JavaScript描述讀書筆記(js實現連結串列-雙向連結串列)
雙向連結串列 雙向連結串列的 remove() 方法比單向連結串列的效率更高,因為不需要再查詢前驅節點了 //建立建構函式建立節點 function Node(element){ this.element = element; this.next = null; th
資料結構-----------線性表(下篇)之雙向連結串列
//----------雙向連結串列的儲存結構------------ typedef struct DuLNode { ElemType date; struct DoLNode *prior; struct DoLNode *next; } DoLNode,*DoLinkList;
python 資料結構與演算法 day02 雙向連結串列
1.實現雙向連結串列 #_+_coding:utf-8_*_ #author: xuanxuan #Time : 2018/11/7 8:48 class Node(): def __init__(self,item): self.item=item
大話資料結構(四)——雙向連結串列的java實現
在實現了單向連結串列後,我們在使用單向連結串列中會發現一個問題:在單向連結串列中查詢某一個結點的下一個結點的時間複雜度是O(1),但是查詢這個結點的上一個結點的時候,時間複雜度的最大值就變成了O(n),因為在查詢這個指定結點的上一個結點時又需要從頭開始遍歷。 那麼該如何解決這個困難呢?
java資料結構——雙向連結串列
連結串列是非常常見的一類線性結構的資料結構,每個節點包含有指標域和資料域,常見的包括單項列表、雙向列表、迴圈列表。這篇文章將詳細介紹雙向連結串列。 雙端連結串列不同於單向連結串列僅有一個指標域指向下一個節點,而是同時持有下一個和上一個指標域,分別指向下一個和上一個節點,如下: 本文
資料結構(c語言)——雙向連結串列的基本操作
定義一個雙向連結串列結構: typedef struct DulNode{ // *prior:前一個元素的地址 // *next:後一個元素的地址 struct DulNode *prior; Element data; struct DulNode *
SDUTOJ-2054 資料結構實驗之連結串列九:雙向連結串列
題目連結 #include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; typedef int ElementType; typedef struct node { ElementType
【資料結構】雙向連結串列的實現
文章目錄 LinkList.h LinkLish.c LinkList.h #ifndef __LINKLIST_H__ #define __LINKLIST_H__ #include <stdio.h>
資料結構-雙向連結串列-插入排序練習題
/* 若線性表中各結點的查詢概率不等,則可用如下策略提高順序查詢的效率:若找到指定的結點,則將該結點的fre域的值加1, 使得經常被查詢的結點位於表的前端。設雙向連結串列的儲存結構有四個域:pre,data,next和fre,data域為字元型,fre域為整形。 設計滿足該功能的
【 C# 資料結構】(一) -------------------------- 泛型帶頭節點的單鏈表,雙向連結串列實現
在程式設計領域,資料結構與演算法向來都是提升程式設計能力的重點。而一般常見的資料結構是連結串列,棧,佇列,樹等。事實上C#也已經封裝好了這些資料結構,在標頭檔案 System.Collections.Generic 中,直接建立並呼叫其成員方法就行。不過我們學習當然要知其然,亦知其所以然。 本文實現的是連結
資料結構與演算法(五)-線性表之雙向連結串列與雙向迴圈連結串列
前言:前面介紹了迴圈連結串列,雖然迴圈連結串列可以解決單鏈表每次遍歷只能從頭結點開始,但是對於查詢某一節點的上一節點,還是頗為複雜繁瑣,所以可以在結點中加入前一個節點的引用,即雙向連結串列 一、簡介 雙向連結串列:在連結串列中,每一個節點都有對上一個節點和下一個節點的引用或指標,即從一個節點出發可以有
自己動手實現資料結構模板(1):雙向連結串列
今天忽然心血來潮,自己動手實現了一個簡單的雙向連結串列和基本功能,大致實現瞭如下功能 dtsListNode為結點類,包括值value、前向指標pre和後向指標next。 dtsList為雙向連結串列,能夠通過begin和end函式獲得首地址指標和指向最後一