根據先序序列和中序,後序和中序序列建立二叉樹
思考:如何才能確定一棵樹?
結論: 通過中序遍歷和先序遍歷可以確定一個樹
通過中序遍歷和後續遍歷可以確定一個樹
通過先序遍歷和後序遍歷確定不了一個樹。
演算法實現:
(一)先序和中序重建二叉樹,按層次遍歷輸出
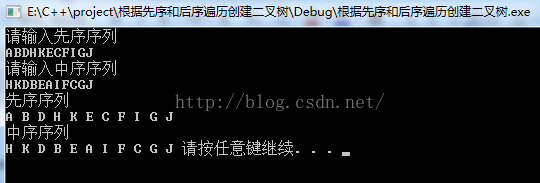
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cmath> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> #include <queue> using namespace std; struct node { char data; node *lchild, *rchild, *mparent; }; node* tmpParent = nullptr; node* CreateBT1(char* pre, char* in, int n) { node* b; char* p; int k; if (n <= 0 || pre == nullptr || in==nullptr) //程式碼魯棒性,細節必須注意 return nullptr; b = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); b->data = *pre; b->mparent = tmpParent; for (p = in; p < in + n; ++p) if (*p == *pre) break; k = p - in; b->lchild = CreateBT1(pre + 1, in, k); b->rchild = CreateBT1(pre + k + 1, p + 1, n - k - 1); return b; } int first_flag = 0; void layerOrder(node * root) { queue<node *> ans; ans.push(root); while (!ans.empty()) { node * tmp = ans.front(); ans.pop(); if (first_flag != 0) { cout << " "; } cout << tmp->data; first_flag = 1; if (tmp->lchild != NULL) ans.push(tmp->lchild); if (tmp->rchild != NULL) ans.push(tmp->rchild); } } void DispBTNode(node* b) { if (b != nullptr) { printf("%c ", b->data); if (b->lchild != NULL || b->rchild != NULL) { DispBTNode(b->lchild); //printf(","); if (b->rchild!=NULL) DispBTNode(b->rchild); //printf(","); } } } int main() { /*for (int i = 0; i<n; i++) { cin >> post[i]; } for (int i = 0; i<n; i++) { cin >> in[i]; }*/ char str1[40] = { 0 }; char str2[40] = { 0 }; printf("請輸入先序序列\n"); scanf("%s", str1); printf("請輸入中序序列\n"); scanf("%s", str2); int n = strlen(str1); node * root; root = CreateBT1((char*)str1, (char*)str2, n); printf("按中序序列將新建的二叉樹輸出\n"); DispBTNode(root); printf("按後序序列將新建的二叉樹輸出\n"); layerOrder(root); return 0; }
(二)根據後序序列和中序序列重建樹,按層次遍歷輸出
關於怎樣由後序和中序重建二叉樹原理讀者可以自己查書,本博文僅供作者自己筆記之用
//程式碼:
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <queue> using namespace std; struct node { char data; node *lchild, *rchild; }; node* CreateBT2(char* post/*指向後序序列開頭的指標*/, char* in/*指向中序序列開頭的指標*/, int n) { char r, *p; int k; if (n <= 0 || post== nullptr || in==nullptr) //程式碼魯棒性,細節必須注意 return nullptr; r = *(post + n - 1); node* b = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); b->data = r; //我們要建立的樹根節點建立好了 for (p = in; p < in + n; ++p) if (*p == r) break; k = p - in; //k是左子樹節點數 b->lchild = CreateBT2(post, in, k); //這兩個語句最關鍵 b->rchild = CreateBT2(post + k, p + 1, n - k - 1); return b; } /****************列印各節點***********************/ int first_flag = 0; void layerOrder(node * root) { queue<node *> ans; ans.push(root); while (!ans.empty()) { node * tmp = ans.front(); ans.pop(); if (first_flag != 0) { cout << " "; } cout << tmp->data; first_flag = 1; if (tmp->lchild != NULL) ans.push(tmp->lchild); if (tmp->rchild != NULL) ans.push(tmp->rchild); } } int main() { int n; cin >> n; char str1[40] = { 0 }; char str2[40] = { 0 }; printf("請輸入先序序列\n"); scanf("%s", str1); printf("請輸入先序序列\n"); scanf("%s", str2); node * root = CreateBT2(str1, str2, n); layerOrder(root); return 0; }
相關推薦
根據先序序列和中序,後序和中序序列建立二叉樹
思考:如何才能確定一棵樹? 結論: 通過中序遍歷和先序遍歷可以確定一個樹 通過中序遍歷和後續遍歷可以確定一個樹 通過先序遍歷和後序遍歷確定不了一個樹。 演算法實現: (一)先序和中序重建二叉樹,
已知一個按先序序列輸入的字元序列,如abc,,de,g,,f,,,(其中逗號表示空節點)。請建立二叉樹並按中序和後序方式遍歷二叉樹,最後求出葉子節點個數和二叉樹深度。
這是一個標準的模板題 記下了就完事了! Input 輸入一個長度小於50個字元的字串。 Output 輸出共有4行: 第1行輸出中序遍歷序列; 第2行輸出後序遍歷序列; 第3行輸出葉子節點個數; 第4行輸出二叉樹深度。 Sample Input abc,,
根據先序序列和中序序列建立二叉樹
思考:如何才能確定一棵樹? 結論: 通過中序遍歷和先序遍歷可以確定一個樹 通過中序遍歷和後續遍歷可以確定一個樹 通過先序遍歷和後序遍歷確定不了一個樹。 單獨先序遍歷:能求解根,但不能求解左子樹什麼時候結束
由先序遍歷和中序遍歷序列建立二叉樹——
Description 按先序順序和中序順序輸入二叉樹的2個遍歷序列,採用二叉連結串列建立該二叉樹並用後序遍歷順序輸出該二叉樹的後序遍歷序列。 Input 輸入資料有多組,對於每組測試資料 第一行輸入二叉樹的先序序列,第二行為中序序列。 Output 對於每組測試資料輸出該二叉樹
根據先序遍歷和中序遍歷建立二叉樹(程式碼)
先宣告一個結構體:二叉樹的三個元素,資料域,左子樹,右子樹。 typedef char ElemType; typedef struct Node { ElemType data; struct Node *lchild,*rchild; }BitTree; 宣告函式:返回
已知中序和先序|後序,建立二叉樹及三種方式遍歷
const int maxv= 10000+10; int n; int in_order[maxv],post_order[maxv],pre_order[maxv]; int lch[maxv],rch[maxv]; //左右子節點 int build1(int L1,
已知二叉樹的中序遍歷結果和(先序或後序結果),還原建立二叉樹
主函式 int main(int argc, char** argv){ int n, m; cin>>n; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ cin>>m; v.push_back(m); } for(
二叉樹 已知前序中序兩個序列,建立二叉樹(中序和後序也有)
本文主要講二叉樹的建樹,具體的說就是,題目給出你二叉樹的前序和中序,你來建樹,還有一個題目是給出中序和後序來建樹 第一題:A binary tree is a finite set of vertices that is either empty or consists
根據先序遍歷和中序遍歷建立二叉樹
演算法思想 先序遍歷的順序是根左右,中序遍歷的順序是左根右。根據這一特性,先序遍歷的第一個元素肯定是根節點。所以我們只要在中序遍歷中找到該根節點的值,根節點以左就是它的左子樹,根節點以右就是它的右子樹,然後就可以遞迴的方式建立二叉樹 假設現在有一顆二叉樹如下
二叉樹——判斷兩棵二叉樹是否相等(先序和中序遍歷序列建立二叉樹)
需求: 利用先序遍歷序列和中序遍歷序列來建立兩棵二叉樹,並判斷是否相等 需要先將建立二叉樹 建立的方法是將該二叉樹的先序的序列和中序的序列分別儲存到Pre陣列和Mid陣列中,它們的儲存順序如下: 判斷兩棵樹是否相等 採用遞迴的方法,用先序,中序
依照先序序列和中序序列建立二叉樹
資料結構上機測試4.1:二叉樹的遍歷與應用1Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536KBProblem Description輸入二叉樹的先序遍歷序列和中序遍歷序列,輸出該二叉樹的後序遍歷序列。Input第一行輸入二叉樹的先序遍歷序列;第二
建立二叉樹,實現二叉樹的先序遍歷、中序和後序遍歷的非遞迴演算法
先序遍歷:若二叉樹為空,則空操作;否則訪問根節點;先序遍歷左子樹;先序遍歷右子樹。 中序遍歷:若二叉樹為空,則空操作;否則中序遍歷左子樹;訪問根節點;中序遍歷右子樹。 後序遍歷:若二叉樹為空,則空操作;否則後序遍歷左子樹;後序遍歷右子樹;訪問根節點。
JAVA 先序、中序、後序、層序,遞迴非遞迴遍歷二叉樹
定義一個二叉樹 package com.niuke.binaryTree; public class binaryTree { int data; binaryTree left; binaryTree right; public binaryTree(int
[LeetCode] Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal 由先序和中序遍歷建立二叉樹
Given preorder and inorder traversal of a tree, construct the binary tree. Note:You may assume that duplicates do not exist in the tree. 這道題要求用先序和中序遍
(1)建立二叉樹的二叉連結串列。 (2)寫出對用二叉連結串列儲存的二叉樹進行先序、中序和後序遍歷的遞迴和非遞迴演算法。 (3)寫出對用二叉連結串列儲存的二叉樹進行層次遍歷演算法。 (4)求二叉樹的所有葉子及結點總數。
(1)建立二叉樹的二叉連結串列。 (2)寫出對用二叉連結串列儲存的二叉樹進行先序、中序和後序遍歷的遞迴和非遞迴演算法。 (3)寫出對用二叉連結串列儲存的二叉樹進行層次遍歷演算法。(4)求二叉樹的所有葉子及結點總數。 include<stdio.h> #inclu
先序和中序建立二叉樹
Given preorder and inorder traversal of a tree, construct the binary tree. Note: You may assume that duplicates do not exist in the tree. /** * Definitio
由中序和後序建立二叉樹,並前序輸出
輸入用例: BAC BCA XDEFAG XEDGAF 輸出用例: ABC FDXEAG 思路與前面那道由前序中序輸出後序思路一樣,前面有詳細的解答 /// /// @file test.c
轉載-由中序和後續序列建立二叉樹
已知某二叉樹具有n(n>0)個不同的節點,其中序序列是a0a1…an-1,後序序列是b0b1…bn-1。 因為在後序遍歷過程中,先遍歷左子樹,再遍歷右子樹,最後訪問根節點。所以,bn-1必定是二叉樹的根節點,而且bn-1也必定在中序序列中出現。也就是說在中序序列中
二叉樹以中序為資料, 先序或者後序為根, 建立二叉樹
#include<iostream> using namespace std; struct Tree{ int v; Tree *left, *right; }; Tree *create_node(int v){ Tree *node = new Tree; node
java由先根中根遍歷序列建立二叉樹,由標明空子樹建立二叉樹,有完全二叉樹順序儲存結構建立二叉鏈式儲存結構
//由先根和中根遍歷建立二叉樹 public class bitree{ public bitree(String preorder,String inorder,int preindex,int in