1099 Build A Binary Search Tree (30 分)dfs、bfs、bst
1099 Build A Binary Search Tree (30 分)
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is recursively defined as a binary tree which has the following properties:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than or equal to the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Given the structure of a binary tree and a sequence of distinct integer keys, there is only one way to fill these keys into the tree so that the resulting tree satisfies the definition of a BST. You are supposed to output the level order traversal sequence of that tree. The sample is illustrated by Figure 1 and 2.
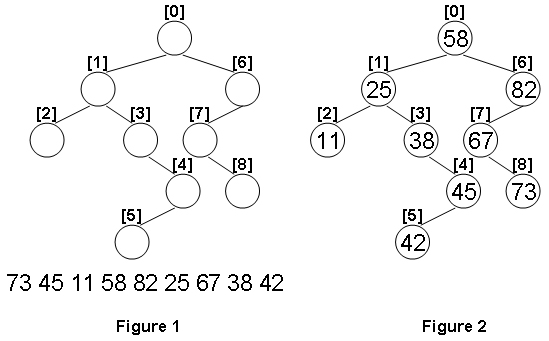
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤100) which is the total number of nodes in the tree. The next N lines each contains the left and the right children of a node in the format left_index right_index, provided that the nodes are numbered from 0 to N−1, and 0 is always the root. If one child is missing, then −1 will represent the NULL child pointer. Finally N distinct integer keys are given in the last line.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in one line the level order traversal sequence of that tree. All the numbers must be separated by a space, with no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
9
1 6
2 3
-1 -1
-1 4
5 -1
-1 -1
7 -1
-1 8
-1 -1
73 45 11 58 82 25 67 38 42
Sample Output:
58 25 82 11 38 67 45 73 42題目大意: 給出樹中每個結點的左右子結點,和一個數據陣列,要求構造出符合的BST(樹的結構要完全對應輸入)。最後輸出該樹的層次遍歷。
解析:先將資料按小到大排序,觀察知道每個結點的左邊結點總數恰好與對應陣列中的下標一致。所以dfs求出左邊孩子結點數,再用dfs模仿先序遍歷構造出樹,最後用bfs輸出層次遍歷結點。該題只要思路清晰就能解決,本人一次AC過了。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
vector<vector<int>> vec;//記錄輸入的左右孩子結點
//arr是原始輸入陣列
//tree對應圖中的樹,下標與資料完全符合
//num是該結點的總孩子結點數,如圖中0結點的孩子總數是8
//lChild該結點的左邊總孩子結點數,如圖中0結點的是5
vector<int> arr,tree,nums,lChild;
int n;
void dfs(int node,int &sum){//計算出該結點的孩子結點數
for(int i=0;i<vec[node].size();i++){
if(vec[node][i] != -1){
sum++;
dfs(vec[node][i],sum);
}
}
}
//構造出BST
void createBST(vector<int> &tree,int node,int low,int high){
tree[node] = arr[low + lChild[node]];
if(vec[node][0] != -1)
createBST(tree,vec[node][0],low,low+lChild[node]-1);
if(vec[node][1] != -1)
createBST(tree,vec[node][1],low +lChild[node]+1,high);
}
void bfs(int node){//層次遍歷輸出結果
queue<int> que;
que.push(node);
int cnt = 0;
while(!que.empty()){
int v = que.front();
que.pop();
cnt++;
printf("%d%s",tree[v],cnt!=n?" ":"");
for(int i=0;i<vec[v].size();i++){
if(vec[v][i] != -1){
que.push(vec[v][i]);
}
}
}
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
vec.resize(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
vec[i].push_back(a);
vec[i].push_back(b);
}
arr.resize(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
cin>>arr[i];
sort(arr.begin(),arr.end());//先按從小到大排序
nums.resize(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int sum = 0;
dfs(i,sum);
nums[i] = sum;//獲得每個結點的總孩子結點數
}
lChild.resize(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int rChild;
if(vec[i][1] == -1)
rChild = 0;
else
rChild = nums[vec[i][1]] + 1;//先求右邊孩子結點數(記得加上它自身)
lChild[i] = nums[i] - rChild;//左邊孩子結點數= 總 - 右邊孩子結點數
}
tree.resize(n);
createBST(tree,0,0,n-1);
bfs(0);
return 0;
} 