排序演算法雜談(五) —— 關於快速排序的優化策略分析
1. 前提
2. 優化策略1:主元(Pivot)的選取
歸併排序(Merge Sort)有一個很大的優勢,就是每一次的遞迴都能夠將陣列平均二分,從而大大減少了總遞迴的次數。
而快速排序(Quick Sort)在這一點上就做的很不好。
快速排序是通過選擇一個主元,將整個陣列劃分(Partition)成兩個部分,小於等於主元 and 大於等於主元。
這個過程對於陣列的劃分完全就是隨機的,俗稱看臉吃飯。
這個劃分是越接近平均二分,那麼這個劃分就越是優秀;而若果不巧取到了陣列的最大值或是最小值,那這次劃分其實和沒做沒有什麼區別。
因此,主元的選取,直接決定了一個快速排序的效率。
通過之前快速排序的學習,我們知道了基本上有兩種主流的劃分方式,我將其稱之為:
- 挖坑取數
- 快慢指標
前者將最左側的數作為主元,後者將最右側的數作為主元,這種行為完全就是隨機取數。
最簡單的的方法,就是在範圍內取一個隨機數,但是這種方法從概率的角度上來說,和之前的沒有區別。
進一步的思考,可以從範圍內隨機取出三個數字,找到三個數字的中位數,然後和原主元的位置進行交換。
將中位數作為主元,相比於隨機取出的另外兩個數字,對於劃分的影響還是很明顯的。
1 package com.gerrard.sort.compare.quick.partition.pivot; 2 3 import com.gerrard.util.RandomHelper; 4 5public final class MediumPivot implements Pivot { 6 7 @Override 8 public int getPivotIndex(int[] array, int left, int right) { 9 int index1 = RandomHelper.randomBetween(left, right); 10 int index2 = RandomHelper.randomBetween(left, right); 11 int index3 = RandomHelper.randomBetween(left, right);12 if (array[index1] > array[index2]) { 13 if (array[index2] > array[index3]) { 14 return index2; 15 } else { 16 return array[index1] > array[index3] ? index3 : index1; 17 } 18 } else { 19 if (array[index1] > array[index3]) { 20 return index3; 21 } else { 22 return array[index2] > array[index3] ? index3 : index2; 23 } 24 } 25 } 26 }
3. 優化策略2:閾值的選取
同樣是參考歸併排序的優化策略,歸併排序可以通過判斷陣列的長度,設定一個閾值。
陣列長度大於閾值的,使用歸併排序策略。
陣列長度小於閾值的,使用直接插入排序。
通過這種方式,歸併排序避免了針對小陣列時候的遞迴(遞迴層次增加最多的場景,就是大量的小陣列),從而減輕了JVM的負擔。
1 public class OptimizedQuickSort implements Sort { 2 3 private ThreeWayPartition partitionSolution = new ThreeWayPartition(); 4 private int threshold = 2 << 4; 5 6 public void setPartitionSolution(ThreeWayPartition partitionSolution) { 7 this.partitionSolution = partitionSolution; 8 } 9 10 public void setThreshold(int threshold) { 11 this.threshold = threshold; 12 } 13 14 @Override 15 public void sort(int[] array) { 16 sort(array, 0, array.length - 1); 17 } 18 19 private void sort(int[] array, int left, int right) { 20 if (right - left < threshold) { 21 insertionSort(array, left, right); 22 } else if (left < right) { 23 int[] partitions = partitionSolution.partition(array, left, right); 24 sort(array, left, partitions[0] - 1); 25 sort(array, partitions[1] + 1, right); 26 } 27 } 28 29 private void insertionSort(int[] array, int startIndex, int endIndex) { 30 for (int i = startIndex + 1; i <= endIndex; ++i) { 31 int cur = array[i]; 32 boolean flag = false; 33 for (int j = i - 1; j > -1; --j) { 34 if (cur < array[j]) { 35 array[j + 1] = array[j]; 36 } else { 37 array[j + 1] = cur; 38 flag = true; 39 break; 40 } 41 } 42 if (!flag) { 43 array[0] = cur; 44 } 45 } 46 } 47 }
4. 優化策略3:三路劃分
從上面的程式碼中,我們可以看到一個 ThreeWayPartition,這就是現在要講的三路劃分。
回顧之前的快速排序劃分的描述:
快速排序是通過選擇一個主元,將整個陣列劃分成兩個部分,小於等於主元 and 大於等於主元。
不難發現,一次劃分之後,我們將原陣列劃分成了三個部分,小於等於主元 and 主元 and 大於等於主元,劃分結束之後,再將主元兩側進行遞迴。
由此可見,等於主元的部分被劃分到了三個部分,那麼我們就有了這樣的思考:
能不能將陣列明確地劃分成三個部分:小於主元 and 主元和等於主元 and 大於主元。
這樣一來,等於主元的部分就直接從下一次的遞迴中去除了。
回看一下 “挖坑取數” 的程式碼:
1 @Override 2 public int partition(int[] array, int left, int right) { 3 int pivot = array[left]; 4 int i = left; 5 int j = right + 1; 6 boolean forward = false; 7 while (i < j) { 8 while (forward && array[++i] <= pivot && i < j) ; 9 while (!forward && array[--j] >= pivot && i < j) ; 10 ArrayHelper.swap(array, i, j); 11 forward ^= true; 12 } 13 return j; 14 }
在內迴圈中,我們的判斷條件是: array[++i] <= pivot。
在這個基礎上,再做一次判斷,針對等於 pivot 的情況,將等於 pivot 的值,與一個已經遍歷過的位置交換:
- 從左往右找大於 pivot 的值時,與陣列開頭部分交換。
- 從右往左找小於 pivot 的值時,與陣列結束部分交換。
那麼,在整個劃分結束之後,我們會得到這麼一個數據模型:
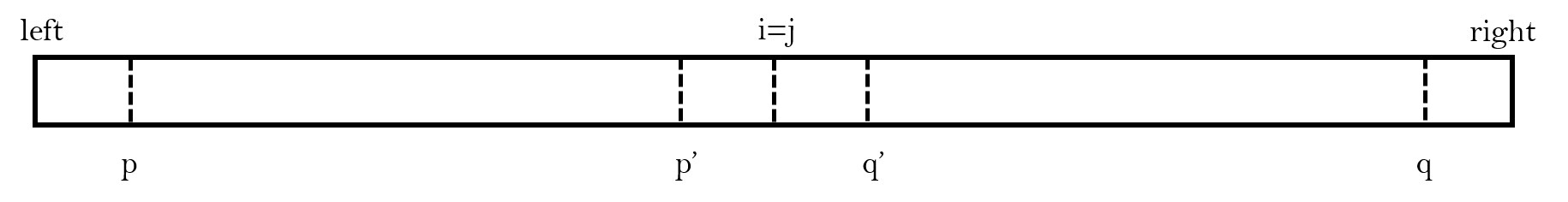
其中:
- 等於 pivot:[left,p) & i & (q,right]
- 小於 pivot:[p,i)
- 大於 pivot:(j,q]
然後將 left->p 的資料依次交換到 i 的左側,同理,將q->right 的資料依次交換到 j 的右側。
這樣我們就能得到整個陣列關於 pivot 的嚴格大小關係:
- 等於 pivot:[p',q']
- 小於 pivot:[left,p')
- 大於 pivot:(q',right]
1 package com.gerrard.sort.compare.quick.partition; 2 3 import com.gerrard.sort.compare.quick.partition.pivot.Pivot; 4 import com.gerrard.util.ArrayHelper; 5 6 /** 7 * Three-Way-partition is an optimized solution for partition, also with complexity O(n). 8 * It directly separate the original array into three parts: smaller than pivot, equal to pivot, larger than pivot. 9 * It extends {@link SandwichPartition} solution. 10 * 11 * Step1: Select the left one as pivot. 12 * Step2: Besides i and j, define two more index p and q as two sides index. 13 * Step3: Work as SandwichPartition, from sides->middle, the only difference is: 14 * when meeting equal to pivot scenario, swap i and p or j and q. 15 * 16 * Step4: After iterator ends, the array should look like: 17 * 18 * left i=j right 19 * --------------------------------------------------- 20 * | | | | | | | 21 * --------------------------------------------------- 22 * p p' q' q 23 * 24 * The distance between left->p and p'->i should be same. 25 * The distance between j->q' and q->right should also be same. 26 * [left,p) and (q,right] is equal to pivot, [p,i) is smaller than pivot, (j,q] is larger than pivot. 27 * 28 * Step5: Exchange [left,p) and [p',i), exchange (q,right] and (j,q']. 29 * Step6: Returns two number p'-1 and q'+1. 30 * 31 */ 32 public final class ThreeWayPartition { 33 34 public int[] partition(int[] array, int left, int right) { 35 if (pivotSolution != null) { 36 int newPivot = pivotSolution.getPivotIndex(array, left, right); 37 ArrayHelper.swap(array, left, newPivot); 38 } 39 int pivot = array[left]; 40 int i = left; 41 int j = right + 1; 42 int p = i; 43 int q = j - 1; 44 boolean forward = false; 45 while (i < j) { 46 while (forward && array[++i] <= pivot && i < j) { 47 if (array[i] == pivot) { 48 ArrayHelper.swap(array, i, p++); 49 } 50 } 51 while (!forward && array[--j] >= pivot && i < j) { 52 if (array[j] == pivot) { 53 ArrayHelper.swap(array, j, q--); 54 } 55 } 56 ArrayHelper.swap(array, i, j); 57 forward ^= true; 58 } 59 while (p > left) { 60 ArrayHelper.swap(array, --p, --i); 61 } 62 while (q < right) { 63 ArrayHelper.swap(array, ++q, ++j); 64 } 65 return new int[]{i, j}; 66 } 67 }
5. 優化測試
最後,針對各種快速排序的演算法,我做了一系列的效能測試:
1 package com.gerrard.helper; 2 3 import com.gerrard.sort.Sort; 4 5 public final class ComparableTestHelper { 6 7 private ComparableTestHelper() { 8 9 } 10 11 public static void printCompareResult(int[] array, Sort... sorts) { 12 for (Sort sort : sorts) { 13 int[] copyArray = ArrayTestHelper.copyArray(array); 14 long t1 = System.nanoTime(); 15 sort.sort(copyArray); 16 long t2 = System.nanoTime(); 17 double timeInSeconds = (t2 - t1) / Math.pow(10, 9); 18 System.out.println("Algorithm " + sort + ", using " + timeInSeconds + " seconds"); 19 } 20 } 21 }
測試結果:

從測試結果中,我們可以發現:
- 取原來的主元,和用隨機數做主元,對於效能的影響完全是隨機的。
- 取中位數做主元,對於效能有著比較明顯的提高。
- 增加閾值,對於效能也有提高,但是閾值選取的數值,還有待深一步的研究。
- 三路快排,在陣列區間較小的情況,對於效能的影響是顯著的,但是陣列區間較大時,對於效能有一定的影響。
- 遞迴轉迭代的方式,能規避StackOverFlow的情況。
但是還有幾個比較奇怪的現象:
- 快速排序,對於陣列內部有很多數字相等的情況,處理情況不佳。
- 快慢指標的方式,對於數字相等的情況,效率降低明顯。
- 挖坑填數的方式,比快慢指標的方式,更容易出現StackOverFlow的情況,而快慢指標似乎通過了某種時間為代價的方式,規避了這種情況。
希望有讀者能夠解惑這些現象。
