A*演算法-第K短路
A*演算法—第K短路
A* 演算法(這裡的* 英文就讀作star),是一種啟發式搜尋的方法,它離我們並不遙遠,常用的BFS就是A*演算法的一種特例。
啟發式搜尋:
DFS與BFS都屬於非啟發式搜尋,又稱盲目型搜尋,它們最大的不同就是啟發式搜尋的選擇不是盲目的,可以通過一個啟發函式進行選擇。
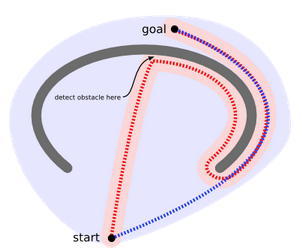
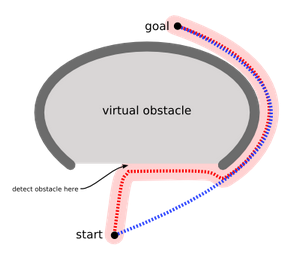
現在看一下下面的兩張圖,就可以很形象的理解了:
假如正常的搜尋方式,我們會不斷移動,直至遇到障礙物,顯然這種方法是很愚蠢的,但是正常的方法的確是這樣進行的,那麼我們就希望擴充套件一個運動演算法,用於對付上圖所示的障礙物。或者避免製造凹形障礙,或者把凹形出口標識為危險的(只有當目的地在裡面時才進去):
A*演算法:
為啟發式演算法中很重要的一種,被廣泛應用在最優路徑求解和一些策略設計的問題中。而A*演算法最為核心的部分,就在於它的一個估值函式的設計上:
f(n)=g(n)+h(n)
其中f(n)是每個可能試探點的估值,它有兩部分組成:一部分為g(n),它表示從起始搜尋點到當前點的代價(通常用某結點在搜尋樹中的深度來表示)。另一部分,即h(n),它表示啟發式搜尋中最為重要的一部分,即當前結點到目標結點的估值,h(n)設計的好壞,直接影響著具有此種啟發式函式的啟發式演算法的是否能稱為A*演算法。
一種具有f(n)=g(n)+h(n)策略的啟發式演算法能成為A演算法的充分條件是:
- 搜尋樹上存在著從起始點到終了點的最優路徑。
- 問題域是有限的。
- 所有結點的子結點的搜尋代價值>0。
- h(n) <= h * (n) (h*(n)為實際問題的代價值)。
一般的搜尋前三條都可以滿足,而第四點就要視情況而定了。
如果上面的概念不能很好理解也沒關係,下面來看一道A*演算法的經典題目,求第K短路【POJ2449】—— [ 題目連結 ]:
Description
“Good man never makes girls wait or breaks an appointment!” said the mandarin duck father. Softly touching his little ducks’ head, he told them a story.
“Prince Remmarguts lives in his kingdom UDF – United Delta of Freedom. One day their neighboring country sent them Princess Uyuw on a diplomatic mission.”
“Erenow, the princess sent Remmarguts a letter, informing him that she would come to the hall and hold commercial talks with UDF if and only if the prince go and meet her via the K-th shortest path. (in fact, Uyuw does not want to come at all)”
Being interested in the trade development and such a lovely girl, Prince Remmarguts really became enamored. He needs you - the prime minister’s help!
DETAILS: UDF’s capital consists of N stations. The hall is numbered S, while the station numbered T denotes prince’ current place. M muddy directed sideways connect some of the stations. Remmarguts’ path to welcome the princess might include the same station twice or more than twice, even it is the station with number S or T. Different paths with same length will be considered disparate.
Input
The first line contains two integer numbers N and M (1 <= N <= 1000, 0 <= M <= 100000). Stations are numbered from 1 to N. Each of the following M lines contains three integer numbers A, B and T (1 <= A, B <= N, 1 <= T <= 100). It shows that there is a directed sideway from A-th station to B-th station with time T.
The last line consists of three integer numbers S, T and K (1 <= S, T <= N, 1 <= K <= 1000).
Output
A single line consisting of a single integer number: the length (time required) to welcome Princess Uyuw using the K-th shortest path. If K-th shortest path does not exist, you should output “-1” (without quotes) instead.
Sample Input
2 2
1 2 5
2 1 4
1 2 2
Sample Output
14
在這道題目中,要求很明確,就是需要你求從s到t的第K短路
第k短路:
K短路的定義:假設從1出發,有M條長度不同的路徑可以到達點N,則K短路就是這M條路徑中第K小的路徑長度。
以上所述,設 f(n) 為 n 節點的過估價函式,則 f(n) = g(n) + h(n); h(n) 就是我們所說的‘啟發式函式’,表示為終點 t 到節點 n 的最佳路徑代價,g(n)表示 g 當前從 s 到 節點 n 所走的實際路徑的長度,即最終結果。
即
估價函式=當前值+當前位置到終點的距離
Solution:
(1)將有向圖的所有邊反向,以原終點t為源點,求解t到所有點的最短距離,即 h(n);
(2)新建一個優先佇列,將源點s加入到佇列中,佇列中維護的是估價函式的值;
(3)從優先順序佇列中彈出 f(p) 最小的點 p,如果點 p 就是 t,則計算t出隊的次數;
如果當前為 t 的第 k 次出隊,則當前路徑的長度就是 s 到 t 的第 k 短路的長度,演算法結束;
否則遍歷與 p 相連的所有的邊,將擴展出的到p的鄰接點資訊加入到優先順序佇列;
Code:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int v;//表示頂點編號
int w;//表示 v 頂點到源點的距離最小值
node(){}
node(int v, int w) : v(v), w(w){}
bool operator < (const node& e) const {
return w < e.w;
}
};
struct Edge{
int u;
int v;
int w;
int next;
Edge(){}
Edge(int u, int v, int w, int next) : u(u), v(v), w(w), next(next){}
};
struct node2{
int v;//表示頂點的編號
int g;//每個頂點的 f(n),表示源點到任意點的距離
int f;//f(n) = g(n) + h(n)
node2(){}
node2(int v, int g, int f) : v(v), g(g), f(f){}
bool operator < (const node2 &x) const{
if(x.f == f)
return x.g < g;
return x.f < f;
}
};
const int maxn = 1005;
const int maxm = 100005;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int N,M,S,E,K,T,first[maxm],first2[maxm],cnt,cnt2;
node dis[maxn];
Edge edge[maxm<<2];
Edge edge2[maxm<<2];
bool vis[maxn];
void init()
{
cnt = cnt2 = 1;//計數-邊的編號
memset(first, -1, sizeof(first));
memset(first2, -1, sizeof(first2));
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
dis[i].w = inf;
dis[i].v = i;
vis[i] = false;
}
}
void addEdge(int u, int v, int w)
{
edge[cnt] = Edge(u, v, w, first[u]);//記錄某個頂點所訪問到的 "前一條邊" 的編號
first[u] = cnt;//不斷的覆蓋某個頂點所訪問到的 "當前的邊" 的編號
cnt++;
}
void addEdge2(int u, int v, int w)
{
edge2[cnt2] = Edge(u, v, w, first2[u]);
first2[u] = cnt2;
cnt2++;
}
void dijstra(int s)//求出 h(n)--任意點到終點 E 的距離
{
dis[s].w = 0;
priority_queue<node> pq;
pq.push(dis[s]);
while(!pq.empty())
{
node now = pq.top();
pq.pop();
int from = now.v;
int cost = now.w;
// if(vis[from]) continue;
// vis[from] = true;
for(int i = first[from]; i != -1; i = edge[i].next)
{
int to = edge[i].v;
if(dis[to].w > edge[i].w + cost)
{
dis[to].w = edge[i].w + cost;
pq.push(dis[to]);
}
}
}
}
int A_star(int s, int t)
{
if(s == t)//始點和終點一樣,必須繞一圈回來
K++;
if(dis[s].w == inf)//始點和終點不可達
return -1;
int num = 0;
priority_queue<node2> pq;//佇列中維護的為f(n)-估價函式的值
pq.push(node2(s, 0, dis[s].w));
while(!pq.empty())
{
node2 e = pq.top();
// cout<<e.v<<" "<<e.g<<" "<<e.f<<endl;
pq.pop();
if(e.v == t)//找到一條最短路,第一次遇到的為最短的,依次為第 k 短路
num++;
if(num == K)//找到第 k 短路
return e.g;
int from = e.v;
int g = e.g;
int f = e.f;
node2 ne;
for(int i = first2[from]; i != -1; i = edge2[i].next)
{
ne.v = edge2[i].v;
ne.g = g + edge2[i].w;
ne.f = ne.g + dis[ne.v].w;
pq.push(ne);
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int from,to,w;
cin>>N>>M;
init();
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
cin>>from>>to>>w;
addEdge(to, from, w);//將邊反向,求出 h(n)--任意點到終點 E 的距離為 dis[]
addEdge2(from, to, w);
}
cin>>S>>E>>K;
dijstra(E);
int ans = A_star(S, E);
printf("%d\n",ans);
return 0;
}
--------------------- 本文來自 Z_Mendez 的CSDN 部落格 ,全文地址請點選:https://blog.csdn.net/z_mendez/article/details/47057461?utm_source=copy