Java多執行緒學習筆記(六) synchronized(this)同步語句塊
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-08
synchronized (this)同步語句塊
1. 一半非同步,一半同步
不在synchronized塊中是非同步執行,在synchronized塊中是同步執行
1.1 Task
public class Task {
public void doLongTimeTask(){
//非同步執行
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++){
System.out.println("not synchronized threadName = " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ " i = " + i);
}
System.out.println("=============================" 1.2 ThreadA
public class ThreadA 1.3 ThreadB
public class ThreadB extends Thread {
private Task task;
public ThreadB(Task task){
super();
this.task = task;
}
@Override
public void run(){
super.run();
task.doLongTimeTask();
}
}
1.4 Test
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Task task = new Task();
ThreadA a = new ThreadA(task);
a.start();
ThreadB b = new ThreadB(task);
b.start();
}
}
1.5 執行結果
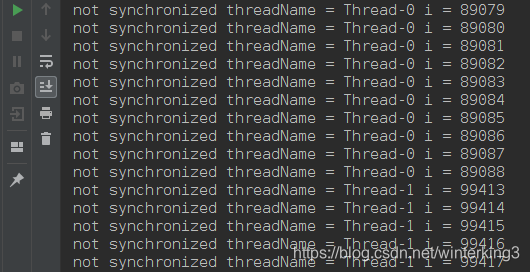
從執行結果看出不在synchronized塊中是非同步執行,在synchronized塊中是同步執行。
2. synchronized程式碼塊間的同步性
當一個執行緒訪問Object的一個synchronized(this)同步程式碼塊時,其他執行緒對這個Object的其他synchronized(this)同步程式碼塊(可以不在同一方法中)或者synchronized方法的訪問將被阻塞,說明synchronized使用的“物件監視器”是同一個。
2.1 ObjectService
public class ObjectService {
public void serviceMehtodA() {
try {
//執行緒A呼叫該程式碼塊,其他的執行緒也不能呼叫這個物件的任何synchronized(this)的程式碼塊
synchronized (this) {
System.out.println("A begin");
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("A end");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void serviceMethodB() {
//只有等到執行緒A呼叫完畢,執行緒B才能呼叫該synchronized(this)程式碼塊
synchronized (this) {
System.out.println("B begin");
System.out.println("B end");
}
}
//synchronized(this)鎖的是物件,所以synchronized方法也會被阻塞
public synchronized void serviceMethodC() {
try {
System.out.println("C begin");
Thread.sleep(500);
System.out.println("C end");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.2 ThreadA
public class ThreadA extends Thread {
private ObjectService service;
public ThreadA(ObjectService service){
super();
this.service = service;
}
@Override
public void run(){
super.run();
service.serviceMehtodA();
}
}
2.3 ThreadB
public class ThreadB extends Thread {
private ObjectService service;
public ThreadB(ObjectService service) {
super();
this.service = service;
}
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
service.serviceMethodB();
}
}
2.4 ThreadC
public class ThreadC extends Thread {
private ObjectService service;
public ThreadC(ObjectService service){
super();
this.service = service;
}
@Override
public void run(){
super.run();
service.serviceMethodC();
}
}
2.5 Test
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ObjectService service = new ObjectService();
ThreadA a = new ThreadA(service);
a.start();
ThreadB b = new ThreadB(service);
b.start();
ThreadC c = new ThreadC(service);
c.start();
}
}
2.6 執行結果
A begin
A end
C begin
C end
B begin
B end
